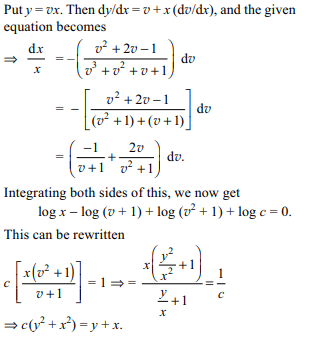1. The solution of
\[\left(\frac{dy}{dx}\right)^{2}+2y \cot x\frac{dy}{dx}=y^{2}\]
is
a) \[y-\frac{c}{1+\cos x}=0\]
b) \[y=\frac{c}{1-\cos x}\]
c) \[x=2\sin^{-1}\sqrt{c/2y}\]
d) Both b and c
Explanation:
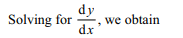
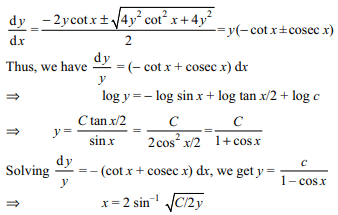
2. The orthogonal trajectories of the system
of curves
\[\left(\frac{dy}{dx}\right)^{2}=\frac{a}{x}\] are
a) \[9a\left(y+C\right)^{2}=4x^{3}\]
b) \[y+C=\frac{-2}{3\sqrt{a}}x^{3/2}\]
c) \[y+C=\frac{2}{3\sqrt{a}}x^{3/2}\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
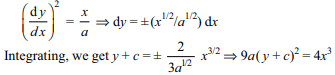
3. A normal is drawn at a point P(x, y) of a
curve. It meets the x-axis at Q. If PQ is of constant length
k. Such a curve passing through (0, k) is
a) a circle with centre (0, 0)
b) \[x^{2}+y^{2}=k^{2}\]
c) \[\left(1+k\right)x^{2}+y^{2}=k^{2}\]
d) Both a and b
Explanation: The equation of normal at P(x, y) is


4. Let f be a non negative function defined on
the interval \[\left[0,\pi/2\right]\] . If
\[\int_{0}^{x} \left(f'\left(t\right)-\sin 2t\right)dt=\int_{x}^{0} f\left(t\right)\tan tdt\]
and f (0) = 1, then
a) f (0) = 1 is the maximum value of f
b) \[f\left(\pi/3\right)=1\]
c) \[\int_{0}^{\pi/2} y dx=3 -\frac{\pi}{2}\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation: Differentiating both sides, we have
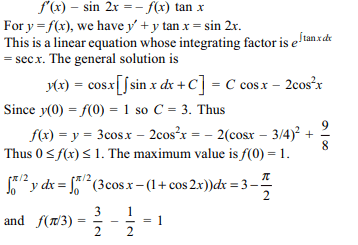
5. The particular solution of
\[t\left(1+t^{2}\right)dx=\left(x+xt^{2}-t^{2}\right)dt, x\mid _{t=1} =-\frac{\pi}{4}\]
is
a) \[x=-t \tan^{-1} t\]
b) \[x=-t \cot^{-1} t\]
c) x = –t tan t
d) x = –t cot t
Explanation:
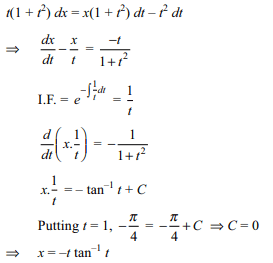
6. General solution of \[y^{2}+x^{2}y'=xyy'\] is
a) \[e^{x/y}=cx\]
b) \[e^{-y/x}=cx\]
c) \[e^{y/x}=cy\]
d) \[e^{x/y}=cy\]
Explanation:
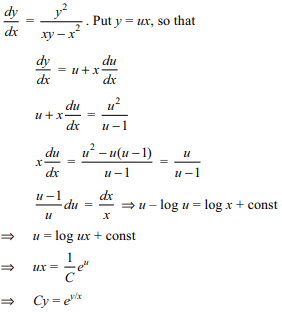
7. If \[y'+\sin\frac{x+y}{2}=\sin\frac{x-y}{2},y\left(0\right)=\pi\]
then
a) \[x=\tan^{-1} e^{-\sin y/2}\]
b) \[y^{2}=4\tan^{-1} e^{-2\sin x/2}\]
c) \[y=2\tan^{-1} e^{-\sin y/2}\]
d) \[y=4\tan^{-1} e^{-2\sin x/2}\]
Explanation:
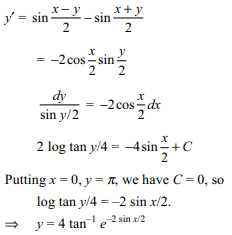
8. The orthogonal trajectories of the family of curves \[a^{n-1}y=x^{n}\] are given by
a) \[x^{n}+n^{2}y=const\]
b) \[ny^{2}+x^{2}=const\]
c) \[n^{2}x+y^{n}=const\]
d) \[n^{2x}-y^{n}=const\]
Explanation:
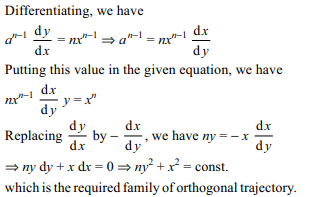
9. The equation of the curve in which subnormal varies
as the square of the ordinate is (k is constant of
proportionality)
a) \[y=Ae^{2kx}\]
b) \[y=e^{kx}\]
c) \[y^{2}/2+kx=A\]
d) \[y^{2}+kx^{2}=A\]
Explanation:
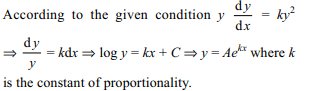
10. The curve satisfying \[y_{1}=\frac{y^{2}-2xy-x^{2}}{y^{2}+2xy-x^{2}}\] and passing through (1,-1) is
a) a straight line
b) a circle
c) an ellipse
d) a parabola
Explanation: