1. A parachutist of weight ‘w’ strikes the ground with his legs fixed and comes to rest with an upward acceleration of magnitude 3 g. Force exerted on him by ground during landing is
a) w
b) 2w
c) 3w
d) 4w
Explanation: Resultant force is w + 3w = 4w
2. At a place where the acceleration due to gravity is \[10m sec^{-2}\] a force of 5 kg-wt acts on a body of mass 10 kg initially at rest. The velocity of the
body after 4 second is
a) 5 \[m sec^{-1}\]
b) 10 \[m sec^{-1}\]
c) 20 \[m sec^{-1}\]
d) 50 \[m sec^{-1}\]
Explanation:
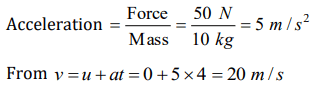
3. In a rocket of mass 1000 kg fuel is consumed at a rate of 40 kg/s. The velocity of the gases ejected from the rocket is \[ 5\times10^{4}m\diagup s\] . The thrust on the
rocket is
a) \[ 2\times10^{3}N\]
b) \[ 5\times10^{4}N\]
c) \[ 2\times10^{6}N\]
d) \[ 2\times10^{9}N\]
Explanation:

4. A man is standing on a weighing machine placed in a lift. When stationary his weight is recorded as 40 kg. If the lift is accelerated upwards with an
acceleration of \[2m\diagup sec^{2}\] , then the weight recorded in the machine will be \[\left(g=10m\diagup sec^{2}\right)\]
a) 32 kg
b) 40 kg
c) 42 kg
d) 48 kg
Explanation: In stationary lift man weighs 40 kg i.e. 400 N.
When lift accelerates upward it's apparent weight = m(g + a) = 40(10 + 2) = 480 N i.e. 48 kg
For the clarity of concepts in this problem kg-wt can be used in place of kg
5. A body of mass 4 kg weighs 4.8 kg when suspended in a moving lift. The acceleration of
the lift is
a) 9.8 \[m sec^{-2}\] downwards
b) 9.8 \[m sec^{-2}\] upwards
c) 1.96 \[m sec^{-2}\] downwards
d) 1.96 \[m sec^{-2}\] upwards
Explanation: As the apparent weight increase therefore we can say that acceleration of the lift is in upward direction.
R = m(g + a)
4.8 g = 4(g + a)
a = 0.2g = 1.96 m /s2
6. An elevator weighing 6000 kg is pulled upward by a cable with an acceleration of \[5m s^{-2}\] . Taking g to be \[10m s^{-2}\] , then the tension in the cable is
a) 6000 N
b) 9000 N
c) 60000 N
d) 90000 N
Explanation: T = m(g + a) = 6000 (10 + 5) = 90000 N
7. A vehicle of 100 kg is moving with a velocity of 5 m/sec. To stop it in \[\frac{1}{10}sec\] , the required force in opposite direction is
a) 5000 N
b) 500 N
c) 50 N
d) 1000 N
Explanation:
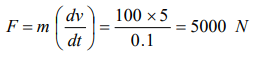
8. A boy having a mass equal to 40 kilograms is standing in an elevator. The force felt by the feet of the boy will be greatest when the elevator
\[\left(g=9.8 metres\diagup sec^{2}\right)\]
a) Stands still
b) Moves downward at a constant velocity of 4 metres/sec
c) Accelerates downward with an acceleration equal to 4 \[ metres\diagup sec^{2}\]
d) Accelerates upward with an acceleration equal to 4 \[ metres\diagup sec^{2}\]
Explanation: Accelerates upward with an acceleration equal to 4 \[ metres\diagup sec^{2}\]
9. A rocket has an initial mass of \[20\times 10^{3}kg\] . If it is to blast off with an initial acceleration of \[4 ms^{-2}\] , the initial thrust needed is \[\left(g\cong10 ms^{-2}\right)\]
a) \[6\times 10^{4}N\]
b) \[28\times 10^{4}N\]
c) \[20\times 10^{4}N\]
d) \[12\times 10^{4}N\]
Explanation:
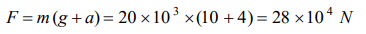
10. The ratio of the weight of a man in a stationary lift and when it is moving downward with uniform acceleration ‘a’ is 3 : 2. The value of ‘a’ is
(g-Acceleration due to gravity of the earth)
a) \[\frac{3}{2}g\]
b) \[\frac{g}{3}\]
c) \[\frac{2}{3}g\]
d) g
Explanation:
