1. The favourable conditions for a spontaneous reaction are
a) \[T\triangle S>\triangle H,\triangle H=+Ve,\triangle S=+Ve\]
b) \[T\triangle S<\triangle H,\triangle H=+Ve,\triangle S=-Ve\]
c) \[T\triangle S=\triangle H,\triangle H=-Ve,\triangle S=-Ve\]
d) \[T\triangle S=\triangle H,\triangle H=+Ve,\triangle S=+Ve\]
Explanation: \[\triangle\]G = \[\triangle\]H -T\[\triangle\]S, \[\triangle\]H + ve, \[\triangle\]S is + ve; T\[\triangle\]S > \[\triangle\]H for spontaneous process. It will make \[\triangle\]G, –ve
2. Identify the correct statement regarding entropy
a) At absolute zero temperature, entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken to be zero
b) At absolute zero temperature, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is positive
c) Absolute entropy of a substance cannot be determined
d) At 0°C, the entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is taken to be zero
Explanation: Third law of Thermodynamics
3. For which of the following process, \[\triangle S\] is negative?
a) \[H_{2}\left(g\right)\rightarrow 2H\left(g\right)\]
b) \[N_{2}\left(g\right)\left(1atm\right)\rightarrow N_{2}\left(g\right)\left(8atm\right)\]
c) \[2SO_{3}\left(g\right)\rightarrow 2SO_{2}\left(g\right)+O_{2}\left(g\right)\]
d) \[C_{\left(diamond\right)}\rightarrow C_{\left(graphite\right)}\]
Explanation: High pressure reduces volume, decreases entropy, hence \[\triangle\]S negative.
4. According to second law of thermodynamics a process (reaction) is spontaneous if during the process
a) \[\triangle S_{universe}>0\]
b) \[\triangle S_{universe}=0\]
c) \[\triangle S_{system}>0\]
d) \[\triangle S_{universe}=\triangle S_{system}\]
Explanation: For spontaneous process, \[\triangle\]Stotal is +ve
5. The law formulated by Nernst is
a) first law of thermodynamics
b) second law of thermodynamics
c) third law of thermodynamics
d) Both (a) and (b)
Explanation: Third law of thermodynamics is due to Nernst
6. If 900 J/g of heat is exchanged at boiling point of water, then what is increase in entropy?
a) 43.4 J/mole
b) 87.2 J/mole
c) 900 J/mole
d) Zero
Explanation:
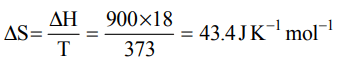
7. Given the following entropy values \[\left( JK^{-1}mol^{-1}\right)\] at 298 K and 1 atm : \[H_{2} \left(g\right): 130.6, Cl_{2}\left(g\right): 223.0\] and HCl(g): 186.7. The entropy
change \[\left( JK^{-1}mol^{-1}\right)\] for the reaction
\[H_{2}\left(g\right)+Cl_{2}\left(g\right)\rightarrow 2HCl\left(g\right)\]
a) +540.3
b) 727.0
c) –166.9
d) 19.8
Explanation:
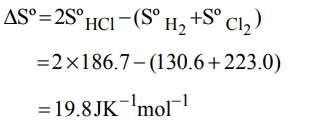
8. Entropy change involved in the conversion of 1 mole of liquid water at 373 K to vapour at the same temperature will be \[\left(\triangle H_{vap.}=2.257kJ /g\right)\]
a) 0.119 kJ
b) 0.109 kJ
c) 0.129 kJ
d) 0.12 kJ
Explanation:
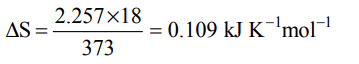
9.Which relation is correct ?
a) \[\triangle G=\triangle H -T\triangle S\]
b) \[\triangle G=\triangle H +T\triangle S\]
c) \[\triangle G=T\triangle S-\triangle H \]
d) \[\triangle G=\triangle H- SdT\]
Explanation: \[\triangle\]G=\[\triangle\]H-T\[\triangle\]S
10. The value of free energy change at equilibrium is
a) positive
b) negative
c) zero
d) not definite
Explanation: At equilibrium, \[\triangle\]G =0