1.If Qs is heat supplied by the steam and Qf is the heat evolved in the feed, then the overall heat transfer coefficient can be represented as? Here AF = Area of film and AW = Area of wall.
a) U = Qf/AW ΔT
b) U = Qs/AF ΔT
c) U = (Qs – Qf)/AW ΔT
d) U = (Qs – Qf)/AF ΔT
Explanation:The heat transfer rate is equal to the heat loss in feed and heat supplied by the steam, which is Qs = Qf = UAW ΔT.
2. What is the amount of heat that needs to be supplied in order to evaporate 10kg of water from a feed of 50kg at a temperature of 25℃ to a final temperature of 150℃?
Latent heat of vaporization of water = 2,260 kJ/kg
Specific heat capacity of solution = 4 KJ/Kg K
a) 52600 KJ
b) 56200 KJ
c) 2272.6 MJ
d) 47600 KJ
Explanation:The total energy required is = mTSΔT + mL = 50×4×125 + 10×2260 = 47600 KJ.
3. What is the overall heat transfer coefficient of an evaporator setup of internal diameter is 30cm and 1m length cylinder in order to evaporate 10kg of water from a feed of 50kg at a temperature of 25℃ to a final temperature of 150℃? Saturated temperature of steam = 160℃
Latent heat of vaporization of water = 2,260 kJ/kg
Specific heat capacity of solution = 4 KJ/Kg K
a) 503 kJ/m2 K
b) 553 kJ/m2 K
c) 5553 kJ/m2 K
d) 5053 kJ/m2 K
Explanation:The heat transferred can be calculated as Q = mTSΔT + mL = 50×4×125 + 10×2260 = 47600 KJ = Q = UAW ΔT = U(πDL)(160-150)=9.42U kJ or U=\(\frac{47600}{9.42}\)=5053 kJ/m2K.
4. Given the overall heat transfer coefficient of the wall is 4053 kJ/m2 K, the internal diameter is 30cm and the length of evaporator is 1m. The evaporator is used to evaporate 10kg of water from a feed of 50kg at a temperature of 25℃ to a final temperature of 150℃. What is the heat transfer area of the setup?
Saturated temperature of steam = 160℃
Latent heat of vaporization of water = 2,260 kJ/kg
Specific heat capacity of solution = 4 KJ/Kg K
a) 1.10m2
b) 1.27m2
c) 2.17m2
d) 1.17m2
Explanation:The heat transferred can be calculated as Q = mTSΔT + mL = 50×4×125 + 10×2260 = 47600 KJ = Q = UAW ΔT = U(A)(160-150)=40530A kJ or A=\(\frac{47600}{40530}\)=1.17m2.
5. Why is the calculated heat transfer area more than the inner surface heat transfer area of the evaporator?
a) Because the area is outer surface area
b) Because the area is equivalent to a large diameter
c) Because the area is on a diameter between outer and inner diameter
d) Area is more than outer surface area
Explanation: Yes, the given statement “Because the area is on a diameter between outer and inner diameter” is correct because the equivalent heat transfer area for the steam part is larger than the feed part, hence the calculation gives us an intermediate value.
6.If the mole fraction of solutes in the feed is XF and in product is XP, then which one of the following relation is correct?
E = evaporate release rate
P = product formation rate
F = Feed supply rate
a) E = \(\frac{P (X_P – X_F)}{X_F}\)
b) E = \(\frac{F (X_P – X_F)}{X_F}\)
c) E = \(\frac{P (X_F – X_P)}{X_P}\)
d) E = \(\frac{F (X_F – X_P)}{X_P}\)
Explanation: The enthalpy mole fraction balance yields us XFE = P(XF – XP) or E = \(\frac{P (X_P – X_F)}{X_F}\).
7. If the mole fraction of solutes in the feed is 0.2 and in product is 0.75, then what is the evaporate formation rate if product formation rate is = 15kg/hr?
a) 45.25 kg
b) 44.25 kg
c) 41.25 kg
d) 43.25 kg
Explanation: The enthalpy mole fraction balance yields us E = \(\frac{P(X_F – X_P)}{X_F}\) = 15 (0.75 – 0.2)/0.2 = 41.25 kg.
8. The straight line in the enthalpy concentration diagram is known as ___________
a) Dew line
b) Azeotropic line
c) Auxiliary line
d) Boiling line
Explanation: The dew line in the EC diagram is the straight line with a negative slope running down the plot.
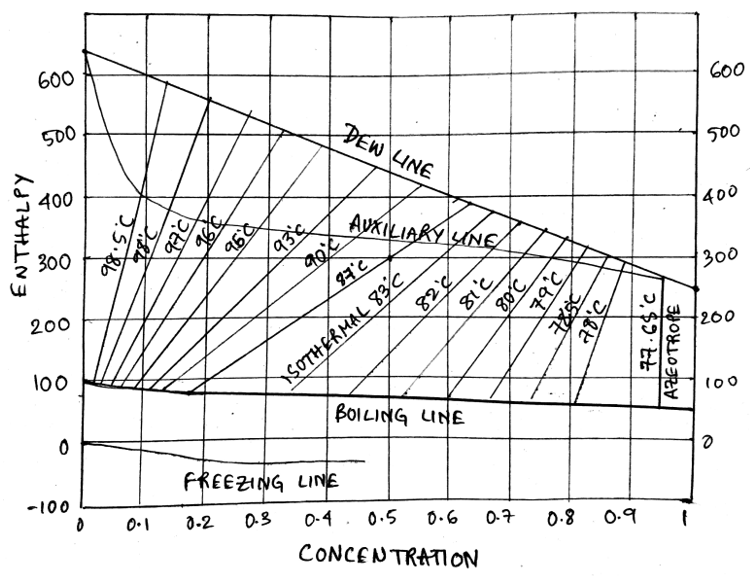
9. What is the name of the line that joins the Dew line to the Boiling line in an enthalpy concentration diagram?
a) Azeotropic line
b) Isothermal line
c) Auxiliary line
d) Freezing line
Explanation:The given line in red defines the isothermal line which loves left with increasing temperature.
10.The _________ represents the line of 100% secondary liquid concentration in an enthalpy concentration diagram.
a) Top horizontal axis
b) Left vertical axis
c) Right vertical axis
d) Bottom horizontal axis
Explanation: The enthalpy concentration diagram can be represented as given below, Observe that the concentration/mole fraction increases as we go to the right in the diagram.
