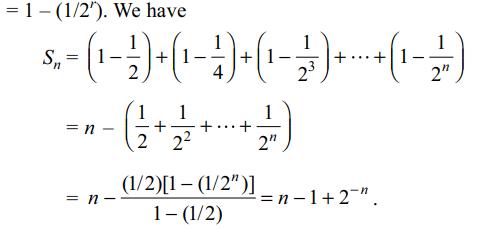1. Let \[a_{k}=\frac{\left(k^{2}+1\right)^{2}}{k^{2}+4} ,k \epsilon N\] , then value of
\[a_1^8a_2^7....a_7^2a_{8}\] is equal to
a) \[\frac{256}{41}\]
b) \[\frac{128}{41}\]
c) \[\frac{64}{41}\]
d) \[\frac{32}{41}\]
Explanation:
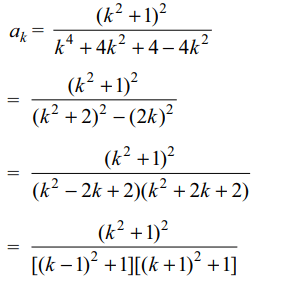
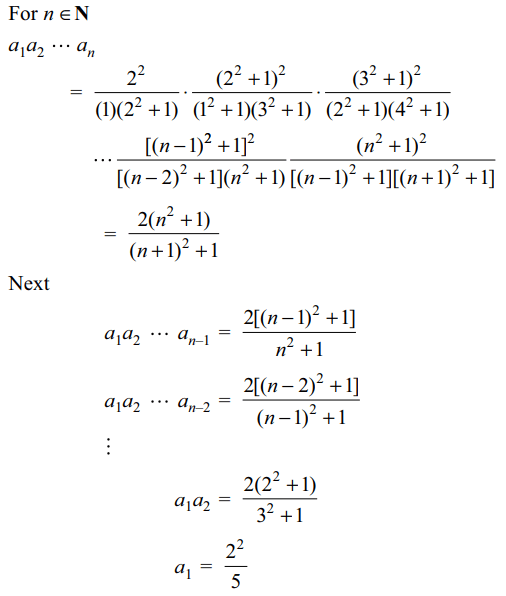
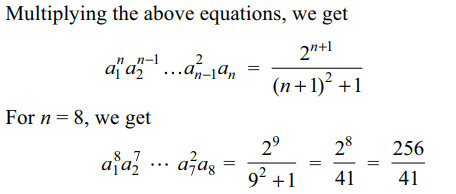
2. Suppose a, b, c are positive real numbers
and that a, b, c are pth, qth, rth terms of a G.P., then least
value of \[E=a^{q-r}+b^{r-p}+c^{p-q}\] is
a) 3
b) 6
c) 9
d) 12
Explanation: As A.M. ≥ G.M
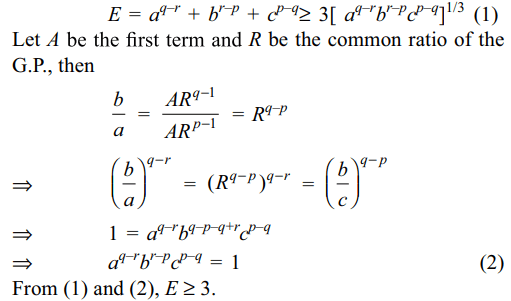
3. Let \[a_{2},a_{2},....a_{n}>0\] be such that
\[\sum_{k=1}^{n}a_{k}=\frac{1}{2}n\left(n+1\right)\] , then least value of \[\sum_{k=1}^{n}\frac{\left(k^{2}-1\right)a_{k}+k^{2}+2k}{a_k^2+a_{k}+1}\]
is
a) \[\frac{1}{2}n^{2}\]
b) \[\frac{1}{2}n\left(n+1\right)\]
c) 2n
d) \[n^{2}-1\]
Explanation:
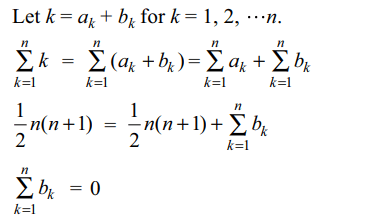
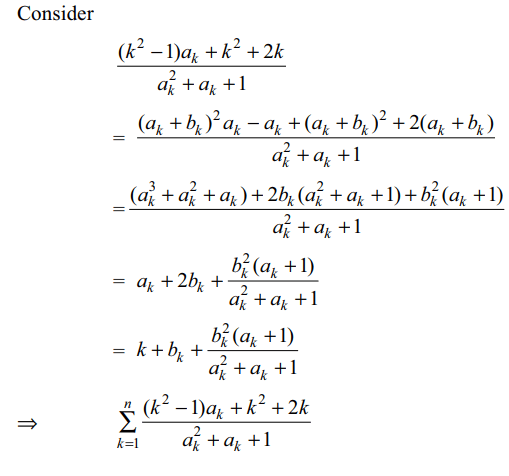
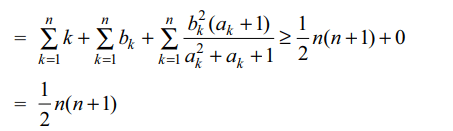
4. Suppose \[a,d \epsilon \left(0,\infty\right)\] and \[a_{n}=a+\left(n-1\right)d\forall n\epsilon N\]
. Least value of \[\sum_{k=1}^{n}\sqrt{a_k^2-a_{k}a_{k+1}+a_{k+1}^2
}\]
is
a) \[\frac{n}{n+1}\sum_{k=1}^{n+1}a_{k}\]
b) \[\frac{1}{n+1}\sum_{k=1}^{n}a_{k}\]
c) \[\frac{n}{n+1}\sum_{k=1}^{n}a_{k}\]
d) \[\frac{n}{n+1}\sum_{k=2}^{n}a_{k}\]
Explanation: For a, b > 0,
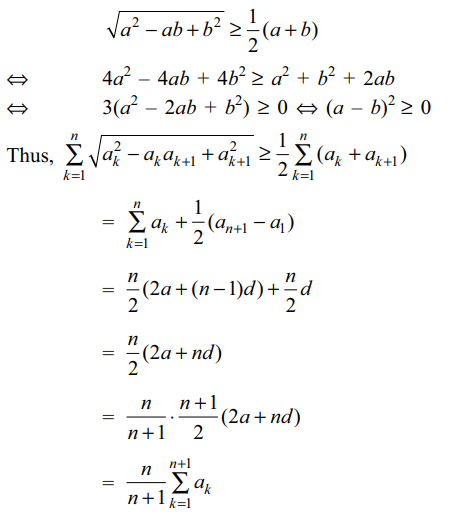
5. Let S denote the set of all real values of
x for which
\[\left(x^{2020}+1\right)\left(1+x^{2}+x^{4}+....+x^{2018}\right)=2020x^{2019}\]
then the number of elements in S is
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) infinite
Explanation:
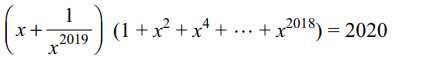
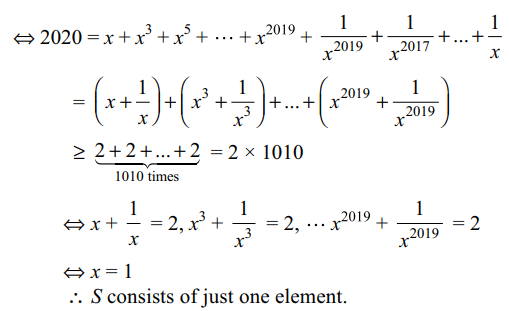
6. Let \[a_{n}=\sum_{k=1}^{n}\frac{1}{k\left(n+1-k\right)}\] , then for \[n\geq 2\]
a) \[a_{n+1}> a_{n}\]
b) \[a_{n+1}< a_{n}\]
c) \[a_{n+1}= a_{n}\]
d) \[a_{n+1}-a_{n}=1/n\]
Explanation:
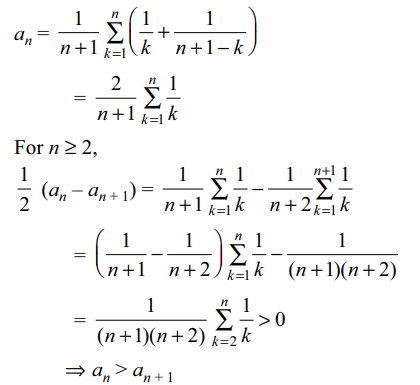
7. If a, b, c are three unequal numbers such
that a, b, c are in A.P. and b – a, c – b, a are in G.P., then ratio
a : b : c is equal
a) 1 : 2 : 3
b) 1 : 3 : 4
c) 2 : 3 : 4
d) 1 : 2 : 4
Explanation: By the hypothesis, b – a = c – b and
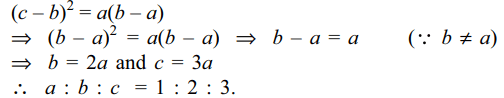
8. If 1, \[\log _{y}x,\log _{z}y,-15\log _{x}z\] are in A.P.,
then
a) \[z^{3}=x\]
b) \[x=y^{-2}\]
c) \[z^{-2}=y\]
d) x=y
Explanation: Let d be the common difference. Then
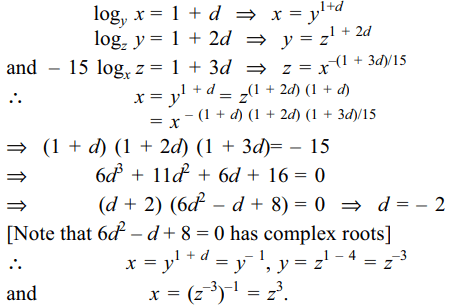
9. If \[\log 2,\log \left(2^{x}-1\right)\] and \[\log \left(2^{x}+3\right)\] are
in A.P., then x is equal to
a) \[\frac{5}{2}\]
b) \[\log _{2}5\]
c) \[\log _{3}2\]
d) \[\frac{3}{2}\]
Explanation:
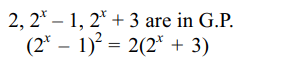
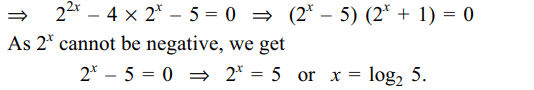
10. The sum \[S_{n}\] to n terms of the series \[\frac{1}{2}+\frac{3}{4}+\frac{7}{8}+\frac{15}{16}+....\]
is equal to
a) \[2^{n}-n-1\]
b) \[1-2^{-n}\]
c) \[2^{-n}+n-1\]
d) \[2^{n}-1\]
Explanation: Let tr denote the rth term of the series. Then tr