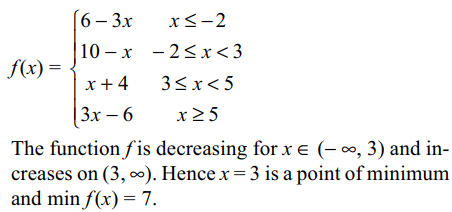1. The tangent to the curve \[y=e^{x}\] drawn at
the point \[\left(c,e^{c}\right)\] intersects the line joining the points \[\left(c-1,e^{c-1}\right)\] and \[\left(c+1,e^{c+1}\right)\]
a) on the left of x = c
b) on the right of x = c
c) at no point
d) at all points
Explanation: Equation of straight line joining A(c + 1, ec+1) and B(c – 1,ec-1) is


2. The function \[y=x/\left(1+x^{2}\right)-\tan^{-1}x\] decreases in the interval
a) (– 1, 1)
b) \[\left[1 ,\infty\right)\]
c) \[\left(-\infty ,-1\right]\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
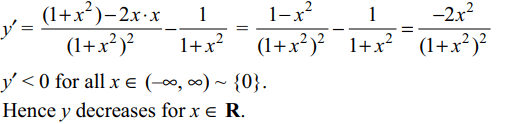
3. The function \[f\left(x\right)=\tan^{-1}x-x-e^{x}\] decreases
in the interval
a) \[\left(1 ,\infty\right)\]
b) \[\left(-1 ,\infty\right)\]
c) \[\left(-\infty ,\infty\right)\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation:

4. For x > 1, y = log x – (x-1) satisfies the
inequality
a) x – 1 > y
b) \[x^{2}-1> y\]
c) \[\frac{x-1}{x}< y\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation: Differentiating the function f(x) = log x – (x – 1), we get
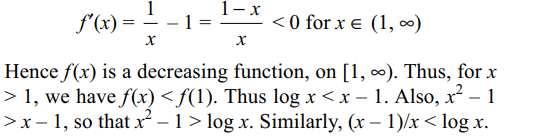
5. Let f be a differentiable function with
range \[\left(0 ,\infty\right)\] and \[g\left(x\right)=\left(f\left(x\right)\right)^{2}-\left(f\left(x\right)\right)^{3}+\left(f\left(x\right)\right)^{4}\]
for
every \[x\epsilon R \] . Then
a) g is increasing whenever f is increasing
b) critical points of g are same as of that of f.
c) g is decreasing whenever f is decreasing
d) All of the Above
Explanation: g'(x) = 2 f(x) f'(x) –3 (f(x))2 f'(x) + 4(f(x))3 f'(x)


6. If \[f\left(x\right)=\begin{cases}3x^{2}+12x-1 & -1\leq x\leq2\\37-x & 2< x \leq3\end{cases}\]
then
a) f(x) is increasing on [–1, 2]
b) f(x) is continuous on [–1, 3]
c) f '(2) doesn’t exist
d) All of the Above
Explanation:
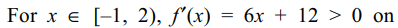
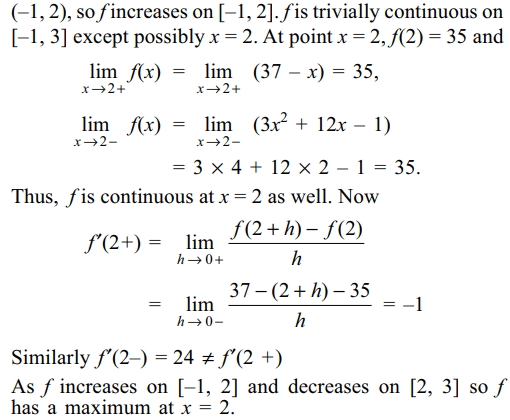
7. If the line aX + bY + c = 0 is a normal to
the curve xy = 1. Then
a) a > 0, b > 0
b) a > 0, b < 0
c) a < 0, b > 0
d) Both b and c
Explanation: Differentiating the equation of curve xy = 1,
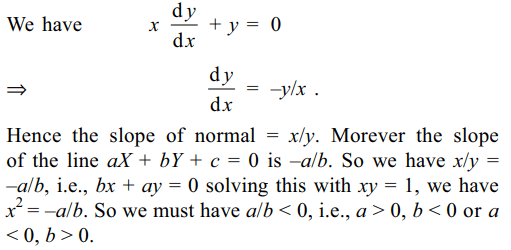
8. The function \[f\left(x\right)=2\log \left(x-2\right)-x^{2}+4x+1\] increases in the interval
a) (1, 2)
b) (2, 3)
c) (5/2, 3)
d) Both b and c
Explanation:


9. The equations of the tangents to the curve
\[y=x^{4}\] from the point (2, 0) not on the curve, are given by
a) y = 0
b) y – 1 = 5(x – 1)
c) \[y-\frac{4098}{81}=\frac{2048}{27}\left(x-\frac{8}{3}\right)\]
d) Both a and c
Explanation: Let (x0, x4 0) be the point of tangency. Then the
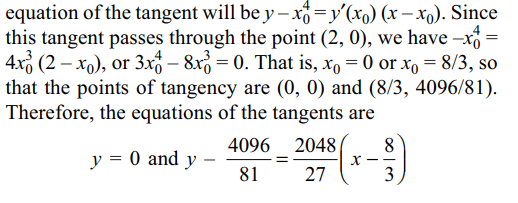
10. The minimum value of
f (x) = |3 - x| + |2 + x| + |5 - x| is
a) 0
b) 7
c) 8
d) 10
Explanation: