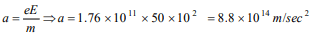1. A charge \[\left(-q\right)\] and another charge \[\left(+Q\right)\] are kept at
two points A and B respectively. Keeping the
charge \[\left(+Q\right)\] fixed at B, the charge \[\left(-q\right)\] at A is
moved to another point C such that ABC forms anequilateral triangle of side l. The net work done in
moving the charge \[\left(-q\right)\] is
a) \[\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}}\frac{Qq}{l}\]
b) \[\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}}\frac{Qq}{l^{2}}\]
c) \[\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}}Qql\]
d) Zero
Explanation:
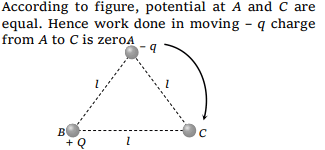
2.A particle of mass ‘m’ and charge ‘q’ is accelerated
through a potential difference of V volt, its energy
will be
a) qV
b) mqV
c) \[\left(\frac{q}{m}\right)V\]
d) \[\frac{q}{mV}\]
Explanation:
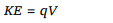
3.Two spheres A and B of radius ‘a’ and ‘b’
respectively are at same electric potential. The
ratio of the surface charge densities of A and B is
a) \[\frac{a}{b}\]
b) \[\frac{b}{a}\]
c) \[\frac{a^{2}}{b^{2}}\]
d) \[\frac{b^{2}}{a^{2}}\]
Explanation:
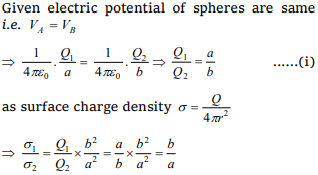
4. Potential at a point x-distance from the centre
inside the conducting sphere of radius R and
charged with charge Q is
a) \[\frac{Q}{R}\]
b) \[\frac{Q}{x}\]
c) \[\frac{Q}{x^{2}}\]
d) xQ
Explanation: Potential at any point inside the charged spherical conductor equals to the potential at the surface of the conductor i.e. Q/R.
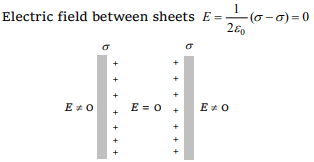
5.Electric field intensity at a point in between two
parallel sheets with like charges of same surface
charge densities \[\left(\sigma\right)\] is
a) \[\frac{\sigma}{2\epsilon_{0}}\]
b) \[\frac{\sigma}{\epsilon_{0}}\]
c) Zero
d) \[\frac{2\sigma}{\epsilon_{0}}\]
Explanation:
6. In an hydrogen atom, the electron revolves
around the nucleus in an orbit of radius
\[0.53\times 10^{-10}m\] . Then the electrical potential
produced by the nucleus at the position of the
electron is
a) – 13.6 V
b) – 27.2 V
c) 27.2 V
d) 13.6 V
Explanation:
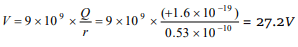
7. Consider two point charges of equal magnitude
and opposite sign separated by a certain distance.
The neutral point due to them
a) Does not exist
b) Will be in mid way between them
c) Lies on the perpendicular bisector of the line
joining the two
d) Will be closer to the negative charge
Explanation: Does not exist
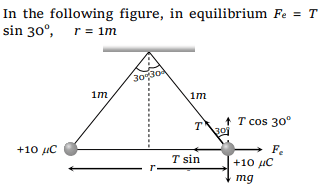
8. Two small spherical balls each carrying a charge
\[Q=10\mu C\] (10 micro-coulomb) are suspended by
two insulating threads of equal lengths 1m each,
from a point fixed in the ceiling. It is found that in
equilibrium threads are separated by an angle
\[60^{\circ}\] between them, as shown in the figure. What
is the tension in the threads \[\left(Given:\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_{o}}=9\times10^{9}Nm/C^{2}\right)\]
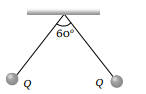
a) 18 N
b) 1.8 N
c) 0.18 N
d) None of the above
Explanation:
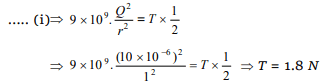
9.A ball of mass 1 g and charge \[10^{-8}C\] moves from
a point A. where potential is 600 volt to the point
B where potential is zero. Velocity of the ball at
the point B is 20 cm/s. The velocity of the ball at
the point A will be
a) 22.8 cm/s
b) 228 cm/s
c) 16.8 m/s
d) 168 m/s
Explanation:
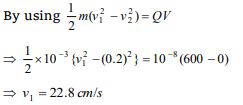
10. The acceleration of an electron in an electric field
of magnitude 50 V/cm, if e/m value of the electron
is \[1.76\times10^{11}C/kg\] , is
a) \[8.8\times10^{14}m/sec^{2}\]
b) \[6.2\times10^{13}m/sec^{2}\]
c) \[5.4\times10^{12}m/sec^{2}\]
d) Zero
Explanation: