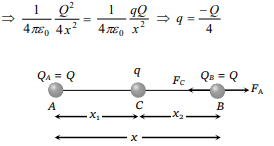1.Two spherical conductors B and C having equal
radii and carrying equal charges in them repel
each other with a force F when kept apart at some
distance. A third spherical conductor having same
radius as that of B but uncharged is brought in
contact with B, then brought in contact with C and
finally removed away from both. The new force of
repulsion between B and C is
a) F/4
b) 3F/4
c) F/8
d) 3F/8
Explanation:

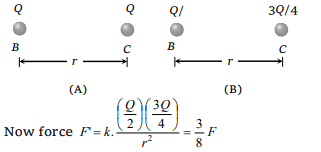
2.The charges on two sphere are \[+7\mu C\] and \[-5\mu C\]
respectively. They experience a force F. If each of
them is given and additional charge of \[-2\mu C\] , the
new force of attraction will be
a) F
b) F/2
c) \[F/\sqrt{3}\]
d) 2F
Explanation:
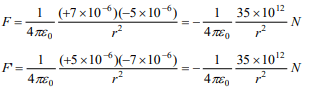
3.The ratio of electrostatic and gravitational forces
acting between electron and proton separated by
a distance \[5\times 10^{-11}m\] will be (Charge on electron = \[1.6\times 10^{-19}C\] , mass of electron = \[9.1\times 10^{-31}kg\] , mass
of proton = \[1.6\times 10^{-27}kg\] , \[G = 6.7\times 10^{-11}Nm^{2}/kg^{2}\] )
a) \[2.36\times 10^{39}\]
b) \[2.36\times 10^{40}\]
c) \[2.34\times 10^{41}\]
d) \[2.34\times 10^{42}\]
Explanation:
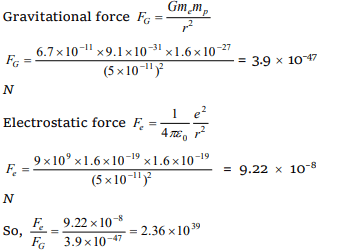
4. Two point charges \[3\times 10^{-6}C\] and \[8\times 10^{-6}C\] repel
each other by a force of \[6\times 10^{-3}N\] . If each of them
is given an additional charge \[-6\times 10^{6}C\] , the force
between them will be
a) \[2.4\times10^{-3}N (attractive)\]
b) \[2.4\times10^{-9}N (attractive)\]
c) \[1.5\times10^{-3}N (repulsive)\]
d) \[1.5\times10^{-3}N (attractive)\]
Explanation:
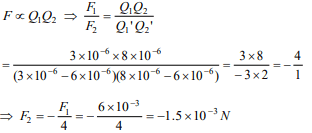
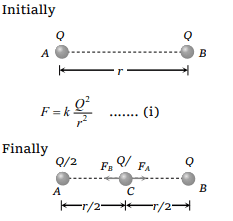
5. Two equally charged, identical metal spheres A
and B repel each other with a force 'F'. The
spheres are kept fixed with a distance 'r' between
them. A third identical, but uncharged sphere C is
brought in contact with A and then placed at the
mid-point of the line joining A and B. The
magnitude of the net electric force on C is
a) F
b) 3F/4
c) F/2
d) F/4
Explanation:
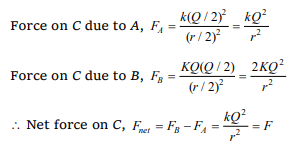
6. Two charges of equal magnitudes and at a
distance r exert a force F on each other. If the
charges are halved and distance between them is
doubled, then the new force acting on each charge
is
a) F / 8
b) F / 4
c) 4 F
d) F / 16
Explanation:
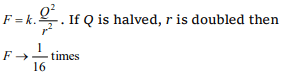
7. An infinite number of charges, each of charge \[1\mu C\] , are placed on the x-axis with co-ordinates \[x =1, 2, 4, 8, ....\infty.\] If a charge of 1 C is kept at the
origin, then what is the net force acting on 1 C
charge
a) 9000 N
b) 12000 N
c) 24000 N
d) 36000 N
Explanation:
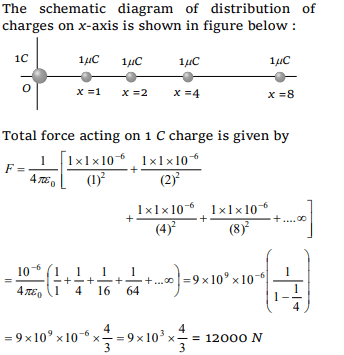
8.The number of electrons in 1.6 C charge will be
a) \[10^{19}\]
b) \[10^{20}\]
c) \[1.1\times10^{19}\]
d) \[1.1\times10^{2}\]
Explanation:
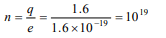
9.Four metal conductors having different shapes
1. A sphere
2. Cylindrical
3. Pear
4. Lightning conductor
are mounted on insulating stands and charged.
The one which is best suited to retain the charges
for a longer time is
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation: In case of spherical metal conductor the charge quickly spreads uniformly over the entire surface because of which charges stay for longer time on the spherical surface. While in case of non-spherical surface, the charge concentration is different at different points due to which the charges do not stay on the surface for longer time.
10. A charge q is placed at the centre of the line
joining two equal charges Q. The system of the
three charges will be in equilibrium, if q is equal
to
a) \[-\frac{Q}{2}\]
b) \[-\frac{Q}{4}\]
c) \[+\frac{Q}{4}\]
d) \[+\frac{Q}{2}\]
Explanation: