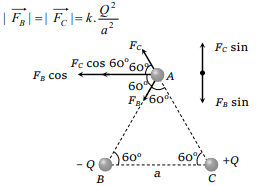
1. Three charges are placed at the vertices of an
equilateral triangle of side ‘a’ as shown in the
following figure. The force experienced by the
charge placed at the vertex A in a direction
normal to BC is
a) \[Q^{2}/\left(4\pi \epsilon_{0}a^{2}\right)\]
b) \[-Q^{2}/\left(4\pi \epsilon_{0}a^{2}\right)\]
c) Zero
d) \[Q^{2}/\left(2\pi \epsilon_{0}a^{2}\right)\]
Explanation: Hence force experienced by the charge at A in the direction normal to BC is zero
2. Two particle of equal mass m and charge q are
placed at a distance of 16 cm. They do not
experience any force. The value \[\frac{q}{m}\]
is
a) l
b) \[\sqrt{\frac{\pi\epsilon_{0}}{G}}\]
c) \[\sqrt{\frac{G}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}}}\]
d) \[\sqrt{4\pi\epsilon_{0}G}\]
Explanation: They will not experience any force if
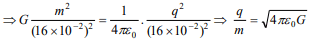
3.When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, it
a) Gains electrons from silk
b) Gives electrons to silk
c) Gains protons from silk
d) Gives protons to silk
Explanation: On rubbing glass rod with silk, excess electron transferred from glass to silk. So glass rod becomes positive and silk becomes negative.
4. An electron is moving round the nucleus of a
hydrogen atom in a circular orbit of radius r. The
coulomb force \[\vec{F}\] between the two is (Where
\[K=\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}}\] )
a) \[-K\frac{e^{2}}{r^{3}}\hat{r}\]
b) \[K\frac{e^{2}}{r^{3}}\vec{r}\]
c) \[-K\frac{e^{2}}{r^{3}}\vec{r}\]
d) \[K\frac{e^{2}}{r^{2}}\hat{r}\]
Explanation:
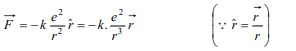
5. A body has – 80 micro coulomb of charge. Number
of additional electrons in it will be
a) \[8\times 10^{-5}\]
b) \[80\times 10^{-17}\]
c) \[5\times 10^{14}\]
d) \[1.28\times 10^{-17}\]
Explanation:
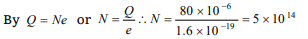
6. Two point charges placed at a certain distance r
in air exert a force F on each other. Then the
distance r' at which these charges will exert the
same force in a medium of dielectric constant k is
given by
a) r
b) r/k
c) \[r/\sqrt{k}\]
d) \[r\sqrt{k}\]
Explanation:
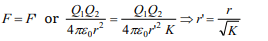
7. Dielectric constant for metal is
a) Zero
b) Infinite
c) 1
d) Greater than 1
Explanation:
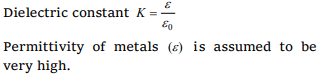
8. A charge of Q coulomb is placed on a solid piece of
metal of irregular shape. The charge will
distribute itself
a) Uniformly in the metal object
b) Uniformly on the surface of the object
c) Such that the potential energy of the system is
minimised
d) Such that the total heat loss is minimised
Explanation: Potential energy depends upon the charge at peaks of irregularities. Since every event in the universe leads to the minimisation of energy.
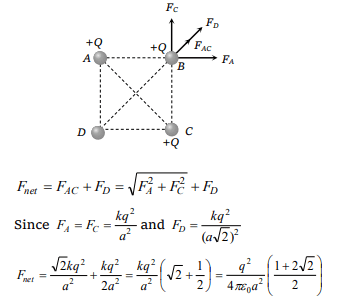
9.Equal charges q are placed at the four corners
A, B, C , D of a square of length a . The magnitude
of the force on the charge at B will be
a) \[\frac{3q^{2}}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}a^{2}}\]
b) \[\frac{4q^{2}}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}a^{2}}\]
c) \[\left(\frac{1+2\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)\frac{q^{2}}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}a^{2}}\]
d) \[\left(2+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\frac{q^{2}}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}a^{2}}\]
Explanation: After following the guidelines mentioned above
10. Two identical conductors of copper and
aluminium are placed in an identical electric
fields. The magnitude of induced charge in the
aluminium will be
a) Zero
b) Greater than in
copper
c) Equal to that in copper
d) Less than in copper
Explanation: Since both are metals so equal amount of charge will induce on them.