1. If A and B are two square matrices of the same
order and m is a positive integer, then
\[\left(A+B\right)^{m}=^{m}C_{0}A^{m}+^{m}C_{1}A^{m-1}B+^{m}C_{2}A^{m-2}B^{2}+....+^{m}C_{m-1}AB^{m-1}+^{m}C_{m}B^{m}\]
if
a) AB = BA
b) AB + BA = O
c) \[A^{m}=O, B^{m}=O\]
d) none of these
Explanation: Binomial theorem is applicable if and only if AB = BA.
2. If \[A\left(\theta\right)=\begin{bmatrix}\cos\theta & -\sin\theta & 0 \\\sin\theta & \cos\theta & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0\end{bmatrix}\]
then \[A\left(\theta\right)^{3}\] will be a
null matrix if and only if
a) \[\theta=\left(2k+1\right)\pi/3,k \epsilon I\]
b) \[\theta=\left(4k-1\right)\pi/3,k \epsilon I\]
c) \[\theta=\left(3k-1\right)\pi/4,k \epsilon I\]
d) none of these
Explanation: Use A( \[\theta\] )3 = A(3 \[\theta\] )
3. If A and B are two non-singular matrices such that
AB = C, then |B| is equal to
a) \[\frac{\mid C\mid}{\mid A\mid }\]
b) \[\frac{\mid A\mid}{\mid C\mid }\]
c) \[\mid C\mid\]
d) none of these
Explanation: Use |AB| = |A| |B|
4. If the system of equations ax + y= 3, x + 2y = 3, 3x
+ 4y = 7 is consistent, then value of a is given by
a) 2
b) 1
c) -1
d) 0
Explanation: From the last two equations we get x = 1, y = 1. This gives a = 2.
5. If the system of equations x + 2y – 3z = 1, (p + 2)z
= 3, (2p + 1) y + z = 2 is consistent, then the value
of p is
a) -2
b) -1/2
c) 0
d) 2
Explanation:
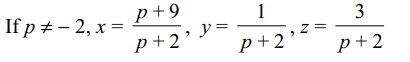
6. The system of linear equations x + y + z = 2, 2x +
y – z = 3, 3x + 2y + kz = 4 has a unique solution if
a) \[ k\neq 0\]
b) – 1 < k < 1
c) – 2 < k < 2
d) k = 0
Explanation:
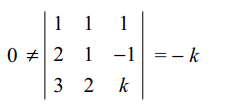
7. If A, B and A + B are non-singular matrices, then
\[\left(A^{-1}+B^{-1}\right)\left[A-A\left(A+B\right)^{-1}A\right]\]
a) O
b) I
c) A
d) B
Explanation:
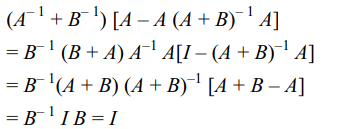
8. If \[\omega \neq 1\] is cube root of unity, and \[A=\begin{bmatrix}1 & \omega & \omega^{2} \\\omega & \omega^{2} & 1 \\\omega^{2} & 1 & \omega\end{bmatrix}\]
is
a) symmetric
b) skew symmetric
c) singular
d) Both a and c
Explanation: |A| = 0
9. Suppose A and B are two \[3 \times3\] non-singular
matrices such that \[\left(AB\right)^{k}=A^{k}B^{k}\]
for k = 2017, 2018, 2019, then
a) \[AB^{-1}A^{-1}=B^{-1}\]
b) \[A^{-2}BA^{2}=\left(A^{-1}BA\right)^{2}\]
c) AB = BA
d) All of the above
Explanation: \[AB^{-1}A^{-1}=B^{-1}\]
10. If A and B are \[3 \times3\] matrices and \[\mid A\mid\neq 0\] , then
a) \[\mid AB\mid= 0\Rightarrow \mid B\mid=0\]
b) \[\mid AB\mid\neq 0\Rightarrow \mid B\mid\neq0\]
c) \[\mid A^{-1}\mid= \mid A\mid^{-1}\]
d) All of the above
Explanation: \[\mid A^{-1}\mid= \mid A\mid^{-1}\]