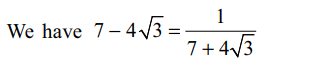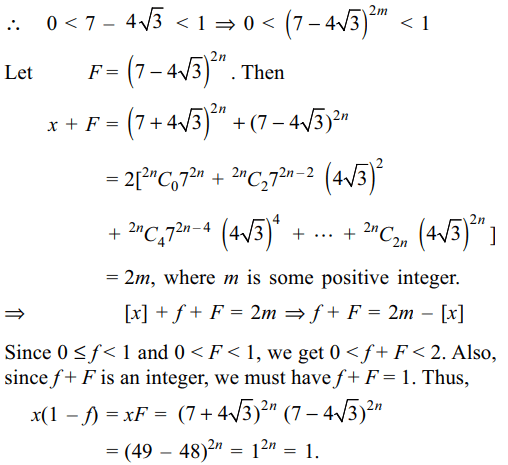1. Suppose \[\alpha,\beta>0\] and
\[x_{n}=^{n}C_{0}\alpha^{n}+^{n}C_{2}\alpha^{n-2}\beta^{2}+....\]
\[Y_{n}=^{n}C_{1}\alpha^{n-1}\beta+^{n}C_{3}\alpha^{n-3}\beta^{3}+....\]
Then
a) \[2x_{n}=\left(\alpha+\beta\right)^{n}+\left(\alpha-\beta\right)^{n}\]
b) \[2y_{n}=\left(\alpha+\beta\right)^{n}-\left(\alpha-\beta\right)^{n}\]
c) \[\lim_{n \rightarrow \infty}\frac{x_{n}}{y_{n}}=1\]
d) All of the above
Explanation:
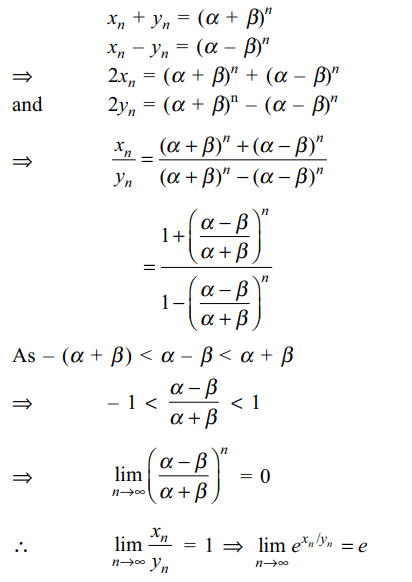
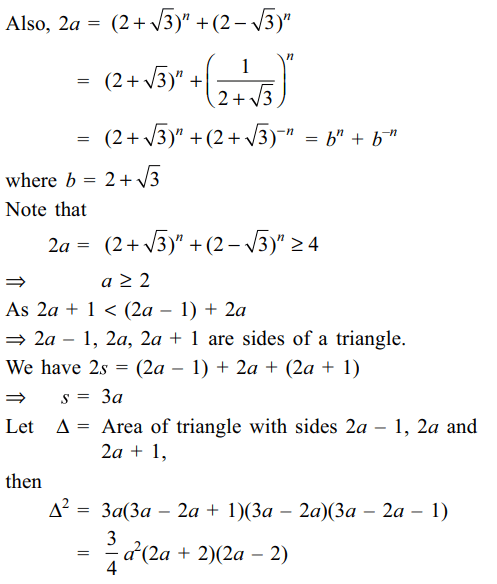
2. Let \[a= \sum_{k\geq0}{\left(\begin{array}{c}n\\ 2k\end{array}\right)}2^{n-2k}3^{k} n \epsilon N , n\geq2\]
then
a) 2a is an integer
b) 2a – 1, 2a, 2a + 1 are sides of a triangle
c) inradius of triangle with sides 2a – 1, 2a,2a+1 is an integer
d) All of the above
Explanation: 2a is clearly an integer
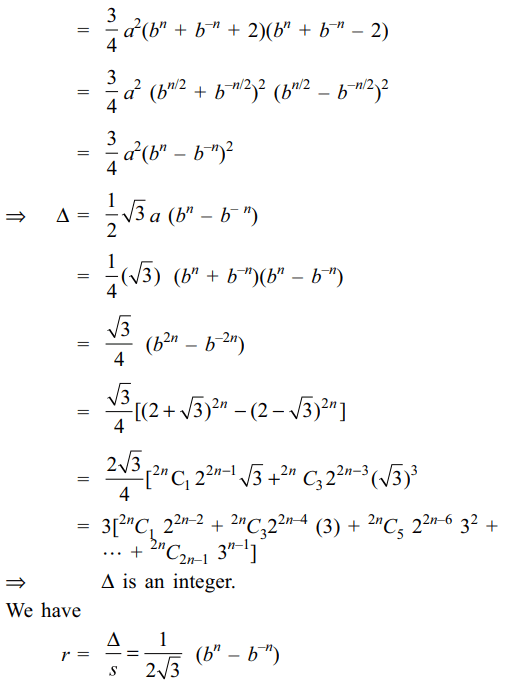
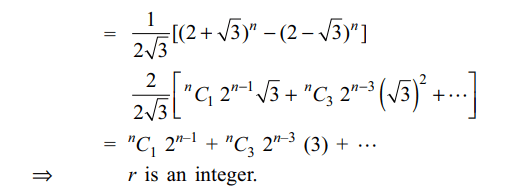
3. Values of x for which the sixth term of the
expansion of \[E= \left(3^{\log_{3}\sqrt{9^{\mid x-2\mid}}}+7^{\left(1/5\right)\log_{7}\left[\left(4\right).3^{\mid x-2\mid}-9\right]}\right)\]
is 567 ,are
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) Both a and c
Explanation:
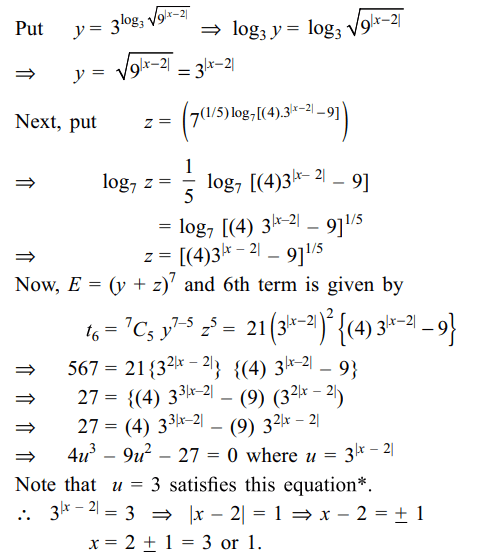
4. If \[C_{r}=\left(\begin{array}{c}n\\ r\end{array}\right)\] , then sum of the series
\[S=C_0^2+\frac{1}{2}C_1^2+\frac{1}{3}C_2^2+....\] upto (n + 1) terms is:
a) \[\frac{1}{n+1}\left(\begin{array}{c}2n+1\\ n+1\end{array}\right)\]
b) \[\frac{1}{2\left(n+1\right)}\left(\begin{array}{c}2n+2\\ n+1\end{array}\right)\]
c) \[\frac{1}{n+1}\left(\begin{array}{c}2n+1\\ n\end{array}\right)\]
d) All of the above
Explanation:
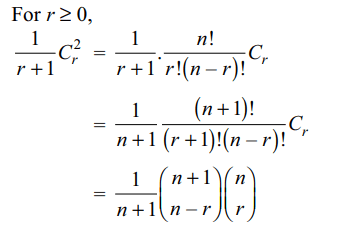
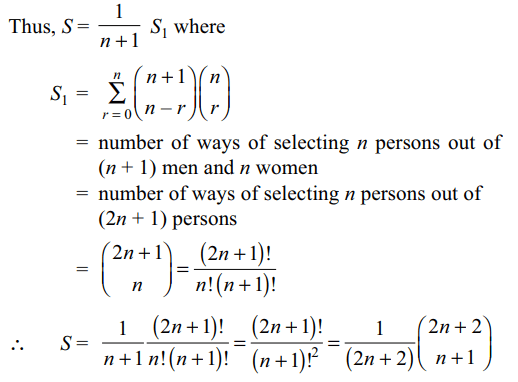
5. Let \[a_{n}=\left(1+\frac{1}{n}\right)^{n}\] . Then for each \[n\epsilon N\]
a) \[a_{n}\geq 2\]
b) \[a_{n}< 3\]
c) \[a_{n}< 4\]
d) All of the above
Explanation: We have a1 = 2 and for n > 2,
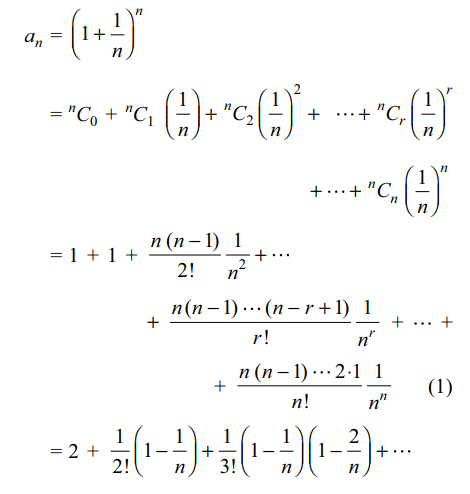
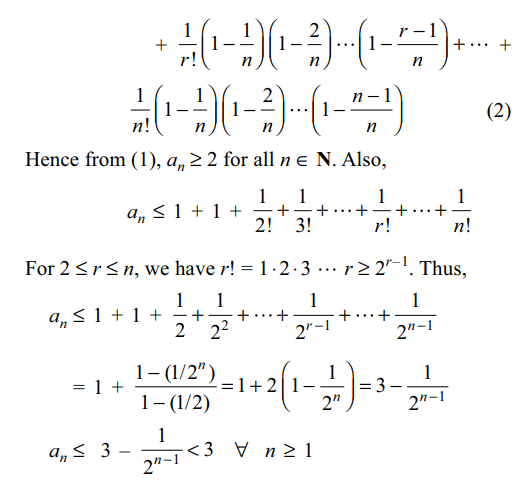
6. If in the expansion of \[\left(\frac{1}{x}+x\tan x\right)^{5}\] the
ratio of 4th term to the 2nd term is
\[\frac{2}{27}\pi^{4}\] , then value of x
can be
a) \[\frac{-\pi}{6}\]
b) \[\frac{-\pi}{3}\]
c) \[\frac{\pi}{3}\]
d) Both b and c
Explanation:
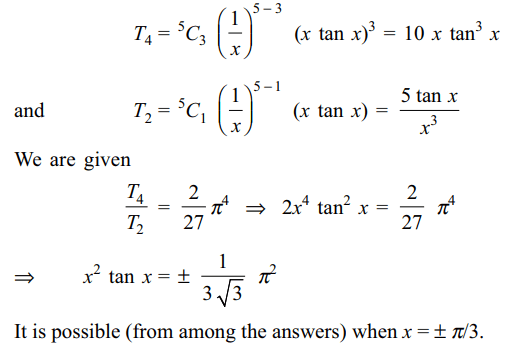
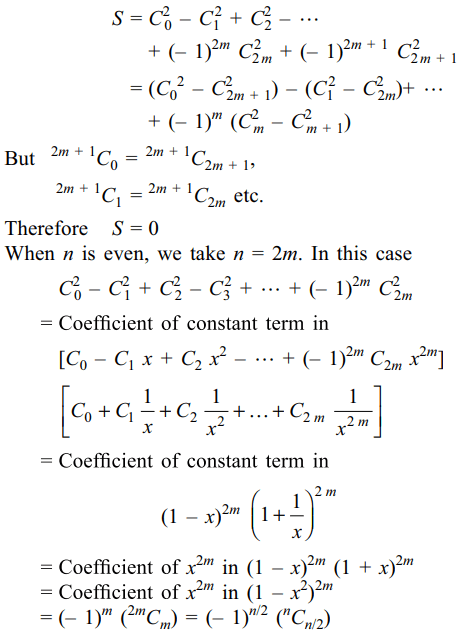
7. The value of the expression \[C_0^2-C_1^2+C_2^2-....+\left(-1\right)^{n}C_n^2\]
is
a) 0 if n is odd
b) \[\left(-1\right)^{n}\] if n is odd
c) \[\left(-1\right)^{n/2}.^{n}C_{n/2}\] if n is even
d) Both a and c
Explanation: When n is odd, taken n = 2m + 1, so that
8. The value of the expression \[C_0^2-2C_1^2+3C_2^2-....+\left(-1\right)^{n}\left(n+1\right)C_n^2\]
is
a) 0 if n is odd
b) \[\left(n+1\right)\left(-1\right)^{n}\] if n is odd
c) \[\left(-1\right)^{n/2}\left(\frac{n}{2}+1\right)\frac{n!}{\left(\frac{n}{2}\right)!\left(\frac{n}{2}\right)!}\]
if n is even
d) Both a and c
Explanation: When n is odd, we take n = 2m – 1, so that
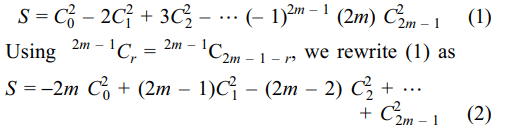
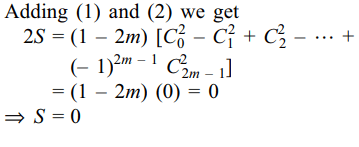
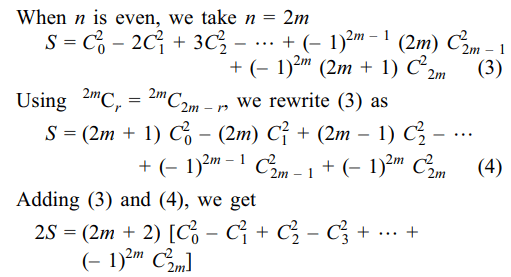
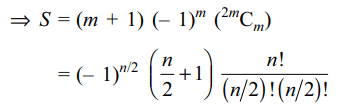
9. If m is a positive integer, then \[\left[\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)^{2m}\right]+1\] ,
where [x] denotes greatest integer \[\leq n\] , is divisible by
a) \[2^{m}\]
b) \[2^{m+1}\]
c) \[2^{m+2}\]
d) Both a and b
Explanation:
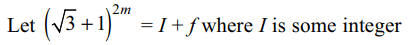
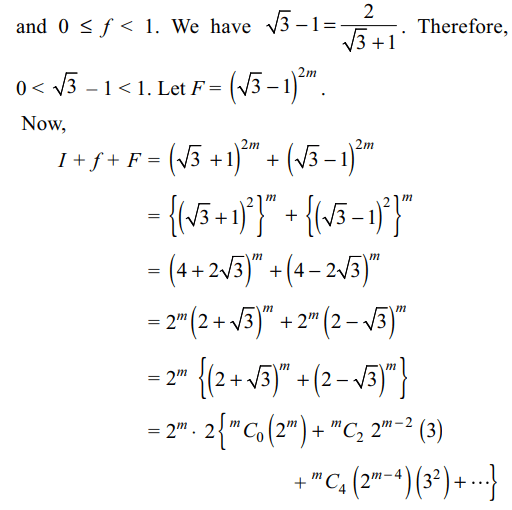
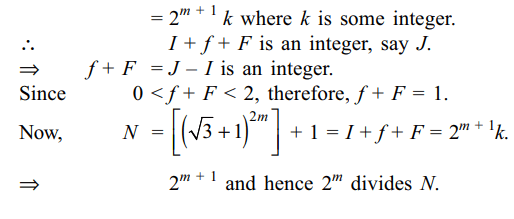
10. If \[x= \left(7+4\sqrt{3}\right)^{2n}=\left[x\right]+f\] then \[x \left(1-f\right)\] is equal to
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation: