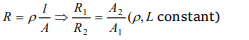1. The resistance of a discharge tube is
a) Ohmic
b) Non-ohmic
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) zero
Explanation: This is because of secondary ionisation which is possible in the gas filled in it
2.We are able to obtain fairly large currents in a
conductor because
a) The electron drift speed is usually very large
b) The number density of free electrons is very
high and this can compensate for the low
values of the electron drift speed and the very
small magnitude of the electron charge
c) The number density of free electrons as well
as the electron drift speeds are very large and
these compensate for the very small
magnitude of the electron charge
d) The very small magnitude of the electron
charge has to be divided by the still smaller
product of the number density and drift speed
to get the electric current
Explanation: The number density of free electrons is very high and this can compensate for the low values of the electron drift speed and the very small magnitude of the electron charge
3.A platinum resistance thermometer has a
resistance of 50Ω at \[20^{\circ}C\] . When dipped in a
liquid the resistance becomes 76.8Ω . The
temperature coefficient of resistance for platinum
is \[\alpha=3.92\times 10^{-3}/^{\circ}C\] . The temperature of the liquid
is
a) \[100^{\circ}C\]
b) \[137^{\circ}C\]
c) \[167^{\circ}C\]
d) \[200^{\circ}C\]
Explanation:
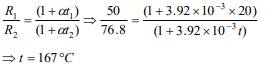
4. In a wire of circular cross-section with radius r,
free electrons travel with a drift velocity V when
a current I flows through the wire. What is the
current in another wire of half the radius and of
the same material when the drift velocity is 2V
a) 2I
b) I
c) I/2
d) I/4
Explanation:

5. The conductivity of a superconductor is
a) Infinite
b) Very large
c) Very Small
d) Zero
Explanation:

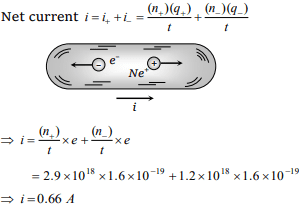
6.In a neon discharge tube \[2.9\times 10^{18}Ne^{+}\] ions move
to the right each second while 1.2 \[\times\] 1018 electrons
move to the left per second. Electron charge is \[1.6\times 10^{-19}C\] . The current in the discharge tube
a) 1 A towards right
b) 0.66 A towards right
c) 0.66 A towards left
d) Zero
Explanation:
7. A steady current flows in a metallic conductor of
non-uniform cross-section. The quantity/ quantities constant along the length of the
conductor is/are
a) Current, electric field and drift speed
b) Drift speed only
c) Current and drift speed
d) Current only
Explanation: If E be electric field, then current density j =

8. The resistivity of \[alloys=R_{alloy}\] ; the resistivity of
constituent metals \[R_{metal}\] . Then, usually
a) \[R_{alloy}=R_{metal}\]
b) \[R_{alloy}< R_{metal}\]
c) There is no simple relation between \[R_{alloy}\] and \[R_{metal}\]
d) \[R_{alloy}>R_{metal}\]
Explanation: \[R_{alloy}>R_{metal}\]
9. Two wires A and B of same material and same
mass have radius 2r and r. If resistance of wire A
is 34Ω , then resistance of B will be
a) 544 Ω
b) 272 Ω
c) 68 Ω
d) 17 Ω
Explanation:
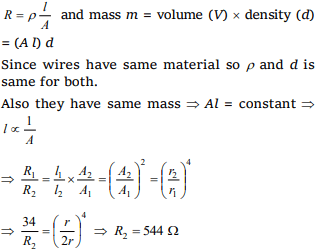
10. Two rods of same material and length have their
electric resistance in ratio 1 : 2 . When both rods
are dipped in water, the correct statement will be
a) A has more loss of weight
b) B has more loss of weight
c) Both have same loss of weight
d) Loss of weight will be in the ratio 1 : 2
Explanation: