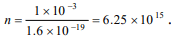1. The drift velocity does not depend upon
a) Cross-section of the wire
b) Length of the wire
c) Number of free electrons
d) Magnitude of the current
Explanation: Length of the wire
2.There is a current of 40 ampere in a wire of
\[ 10^{-6}m^{2}\] area of cross-section. If the number of
free electron per \[ m^{3}\] is \[ 10^{29}\] , then the drift
velocity will be
a) \[1.25\times 10^{3}m/s\]
b) \[2.50\times 10^{-3}m/s\]
c) \[25.0\times 10^{-3}m/s\]
d) \[250\times 10^{-3}m/s\]
Explanation:
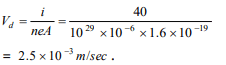
3.At room temperature, copper has free electron
density of \[8.4\times 10^{28} per\] \[m^{3}\] . The copper
conductor has a cross-section of 10–6 m2 and
carries a current of 5.4 A. The electron drift
velocity in copper is
a) 400 m/s
b) 0.4 m/s
c) 0.4 mm/s
d) 72 m/s
Explanation:
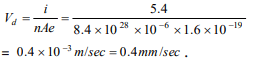
4. The resistance of a 5 cm long wire is 10Ω . It is
uniformly stretched so that its length becomes 20
cm. The resistance of the wire is
a) 160Ω
b) 80 Ω
c) 40 Ω
d) 20Ω
Explanation:
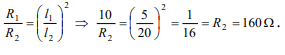
5. The resistance of an incandescent lamp is
a) Greater when switched off
b) Smaller when switched on
c) Greater when switched on
d) The same whether it is switched off or
switched on
Explanation:

6.In the figure a carbon resistor has bands of
different colours on its body as mentioned in the
figure. The value of the resistance is
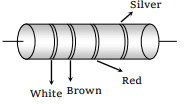
a) 2.2 k Ω
b) 3.3 k Ω
c) 5.6 k Ω
d) 9.1 k Ω
Explanation:
7. By increasing the temperature, the specific
resistance of a conductor and a semiconductor
a) Increases for both
b) Decreases for both
c) Increases, decreases
d) Decreases, increases
Explanation: Increases, decreases
8. Which of the following is vector quantity
a) Current density
b) Current
c) Wattless current
d) Power
Explanation: Current density
9.Masses of 3 wires of same metal are in the ratio 1
: 2 : 3 and their lengths are in the ratio 3 : 2 : 1.
The electrical resistances are in ratio
a) 1 : 4 : 9
b) 9 : 4 : 1
c) 1 : 2 : 3
d) 27 : 6 : 1
Explanation:
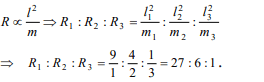
10. A current of 1 mA is flowing through a copper
wire. How many electrons will pass a given point
in one second [ e = 1.6 \[\times\] 10-19 Coulomb]
a) \[6.25\times 10^{19}\]
b) \[6.25\times 10^{15}\]
c) \[6.25\times 10^{31}\]
d) \[6.25\times 10^{8}\]
Explanation: