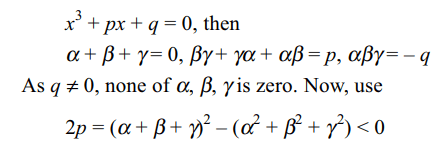1. Let \[\alpha\] and \[\beta\] be the roots of \[x^{2}-6x-2=0\] , with
\[\alpha>\beta\] . If \[a_{n}=\alpha^{n}-\beta^{n}\] for \[n\geq 1\] , then the value of
\[\frac{a_{10}-2a_{8}}{2a_{9}}\]
is
a) 3
b) 2
c) 1
d) 4
Explanation:
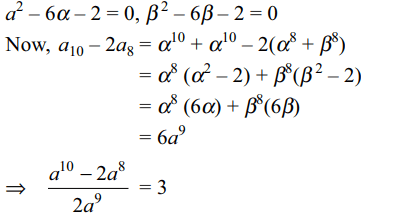
2. A value of b for which the equations
\[x^{2}+bx-1=0\]
\[x^{2}+x+b=0\]
have one root in common is
a) \[-\sqrt{2}\]
b) \[i\sqrt{5}\]
c) \[i\sqrt{3}\]
d) \[\sqrt{2}\]
Explanation:
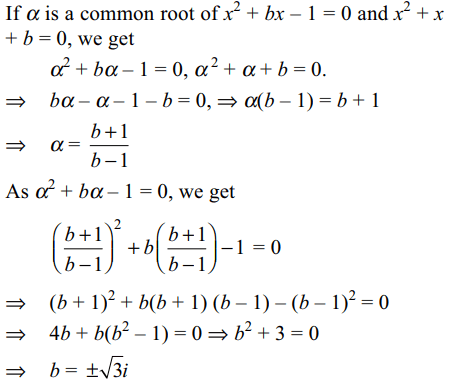
3. If \[x \epsilon R\] , the number of solutions of \[\sqrt{2x+1}-\sqrt{2x-1}=1\] is
a) 0
b) 1
c) 4
d) infinite
Explanation:
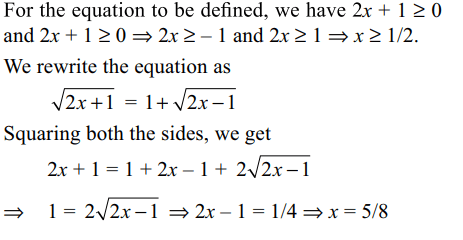

4. If l, m, n are real, \[l+m\neq0\] , then the roots of the
equation
\[\left(l+m\right)x^{2}-3\left(l-m\right)x-2\left(l+m\right)=0\]
a) real and unequal
b) complex
c) real and equal
d) purely imaginary
Explanation:

5. If the equation \[\sqrt{x+1}-\sqrt{x}=a\] has a solution, then
a) 0 < a < 1
b) a > 1
c) \[0 < a \leq 1\]
d) \[ a \leq 1\]
Explanation:
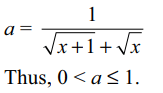
6. Let \[\alpha\] , \[\beta\] be the roots of the equation \[x^{2}-ax+b=0\]
and \[A_{n}=\alpha^{n}+\beta^{n}\] . Then \[A_{n+1}-aA_{n}+bA_{n-1}\] is equal to
a) -a
b) b
c) a-b
d) 0
Explanation:
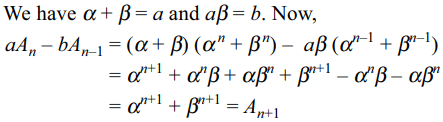
7. If \[\alpha,\beta,\gamma\] are such that \[\alpha+\beta+\gamma=2,\alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}+\gamma^{2}=6,\alpha^{3}+\beta^{3}+\gamma^{3}=8\]
then \[\alpha^{4}+\beta^{4}+\gamma^{4}\] is
a) 5
b) 18
c) 12
d) 36
Explanation:
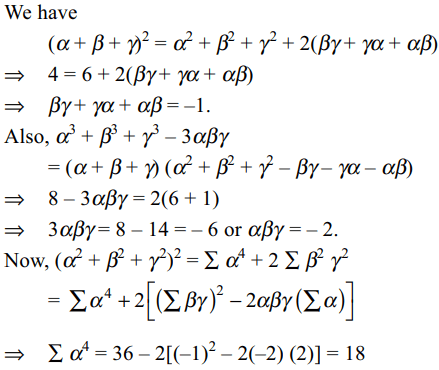
8. In a triangle PQR, \[\angle\] R = \[\pi\] /4. If tan (P/3) and
tan (Q/3) are the roots of the equation ax2 + bx +
c = 0, then
a) a + b = c
b) b + c = 0
c) a + c = b
d) b = c
Explanation:
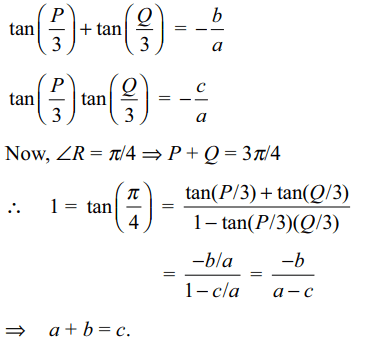
9. The product of the roots of \[\sqrt[3]{8+x}+\sqrt[3]{8-x}=1\] is
a) -21
b) -189
c) -9
d) -5
Explanation:
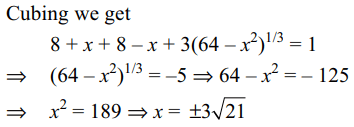
10. If all the roots of \[x^{3}+px+q=0\] p, q \[\epsilon\] R , \[q\neq 0\] are
real, then
a) p < 0
b) p = 0
c) p > 0
d) p > q
Explanation: