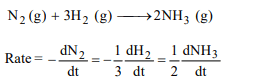1. The rate of a reaction does not depend upon
a) Temperature
b) Concentration
c) Catalyst
d) None of these
Explanation: None of these
2. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a) Activation energy for the forward reaction equals
activation energy for the reverse reaction
b) For a reversible reaction, an increase in temperature
increases the reaction rate for both the forward and
the backward reaction
c) The larger the initial reactant concentration for a
second order reaction, the shorter its
half-life.
d) When \[\triangle t\] is infinitesimally small, the average rate equals
the instantaneous rate
Explanation: "Activation energy for the forward reaction equals activation energy for the reverse reaction". This statement is incorrect.
3. Order of reaction can be
a) 0
b) fraction
c) whole number
d) integer, fraction, zero
Explanation: Order of reaction can be integer, fraction, zero
4.The rate of reaction between two reactants A and B
decreases by a factor of 4 if the concentration of reactant
B is doubled. The order of this reaction with respect to
reactant B is:
a) 2
b) -2
c) 1
d) -1
Explanation: -2
5.The rate of reaction between A and B increases by a factor
of 100, when the concentration of A is increased 10 folds,
the order of reaction with respect to A is
a) 10
b) 1
c) 4
d) 2
Explanation: 2
6. For the reaction \[H_{2}\left(g\right)+Br_{2}\left(g\right)\rightleftharpoons 2HBr\left(g\right)\] , the rate law
is rate =k \[\left[H_{2}\right]\left[Br_{2}\right]^{1/2}\] . Which of the following statement
is true about this reaction
a) The reaction is a second order one
b) Molecularity of the reaction is 3/2
c) The unit of k is \[s^{-1}\]
d) Molecularity of the reaction is 2
Explanation: Molecularity of the reaction is 2
7. In the reversible reaction
\[2NO_{2}\rightleftharpoons N_{2}O_{4},\]
the rate of disappearance of \[NO_{2}\] is equal to
a) \[\frac{2K_{1}}{K_{2}}\left[NO_{2}\right]^{2}\]
b) \[2K_{1}\left[NO_{2}\right]^{2}-2K_{2}\left[N_{2}O_{4}\right]\]
c) \[2K_{1}\left[NO_{2}\right]^{2}-K_{2}\left[N_{2}O_{4}\right]\]
d) \[\left(2K_{1}-K_{2}\right)\left[NO_{2}\right]\]
Explanation:
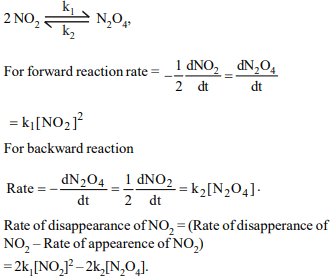
8. The rate of the reaction intermediates can be determined by
the study of
a) catalyst effects
b) concentration of the reactants
c) temperature effects
d) solvent effects
Explanation: By concentration of reactants
9. \[3A\rightarrow 2B\] , rate of reaction, \[\frac{+d\left[B\right]}{dt}\] is equal to
a) \[-\frac{3}{2}\frac{d\left[A\right]}{dt}\]
b) \[-\frac{2}{3}\frac{d\left[A\right]}{dt}\]
c) \[-\frac{1}{3}\frac{d\left[A\right]}{dt}\]
d) \[+2\frac{d\left[A\right]}{dt}\]
Explanation:
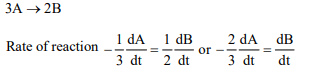
10. Consider the chemical reaction,
\[N_{2}\left(g\right)+ 3 H_{2}\left(g\right)\rightarrow 2NH_{3}\left(g\right)\]
The rate of this reaction
can be expressed in terms of time derivative of concentration
of \[N_{2}\left(g\right) , H_{2}\left(g\right)or NH_{3}\left(g\right)\] . Identify the correct relationship
amongst the rate expressions
a) \[Rate=\frac{-d\left[N_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{-1}{3}\frac{d\left[H_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{1}{2}\frac{d\left[NH_{3}\right]}{dt}\]
b) \[Rate=\frac{-d\left[N_{2}\right]}{dt}=-3\frac{d\left[H_{2}\right]}{dt}=2\frac{d\left[NH_{3}\right]}{dt}\]
c) \[Rate=\frac{d\left[N_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{1}{3}\frac{d\left[H_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{1}{2}\frac{d\left[NH_{3}\right]}{dt}\]
d) \[Rate=\frac{-d\left[N_{2}\right]}{dt}=-\frac{d\left[H_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{d\left[NH_{3}\right]}{dt}\]
Explanation: