1. The reaction \[A\rightarrow B\] follows first order kinetics. The time
taken for 0.8 mole of A to produce 0.6 mole of B is 1 hour.
What is the time taken for conversion of 0.9 mole of A to
produce 0.675 mole of B?
a) 0.5 hour
b) 0.25 hour
c) 2 hour
d) 1 hour
Explanation:
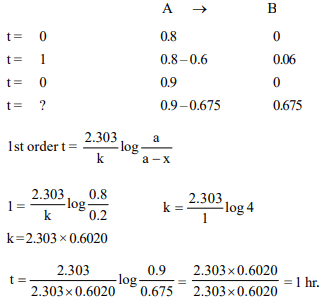
2. According to the adsorption theory of catalysis, the speed
of the reaction increases because
a) in the process of adsorption, the activation energy of
the molecules becomes large
b) adsorption produces heat which increases the speed of
the reaction
c) adsorption lowers the activation energy of the reaction
d) the concentration of product molecules at the active
centres of the catalyst becomes high due to adsorption
Explanation: Adsorption lowers the activation energy
3. The reaction of hydrogen and iodine monochloride is given
as:
\[H_{2}\left(g\right)+2ICl\left(g\right)\rightarrow 2HCl\left(g\right)+I_{2}\left(g\right)\]
The reaction is of first order with respect to \[H_{2}\left(g\right)\] and \[ICl\left(g\right),\] following mechanisms were proposed.
Mechanism A:
\[H_{2}\left(g\right)+2ICl\left(g\right)\rightarrow 2HCl\left(g\right)+I_{2}\left(g\right)\]
Mechanism B:
\[H_{2}\left(g\right)+ICl\left(g\right)\rightarrow HI\left(g\right);slow\]
\[HI\left(g\right)+ICl\left(g\right)\rightarrow HCl\left(g\right)+I_{2}\left(g\right);fast\]
Which of the above mechanism(s) can be consistent with the
given information about the reaction?
a) A and B both
b) neither A nor B
c) A only
d) b only
Explanation:

4. In a first-order reaction \[A\rightarrow B\] , if k is rate constant and inital
concentration of the reactant A is 0.5 M, then the half-life is
a) \[\frac{log2}{K}\]
b) \[\frac{log2}{K\sqrt{0.5}}\]
c) \[\frac{ln 2}{K}\]
d) \[\frac{0.693}{0.5K}\]
Explanation:
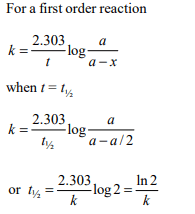
5. If 60% of a first order reaction was completed in 60 minutes,
50% of the same reaction would be completed in aproximately
a) 45 minutes
b) 60 minutes
c) 40 minutes
d) 50 minutes
Explanation:
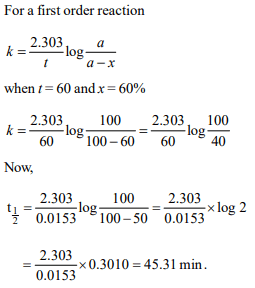
6. The rate constants \[K_{1}\] and \[K_{2}\] for two different reactions are
\[10^{16}.e^{-2000/t}\] and \[10^{15}.e^{-1000/t}\] , respectively. The temperature
at which \[K_{1} = K_{2}\] is :
a) 1000 K
b) \[\frac{2000}{2.303}K\]
c) 2000 K
d) \[\frac{1000}{2.303}K\]
Explanation:
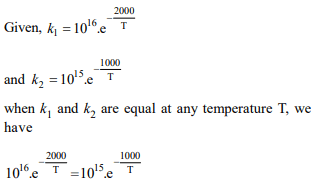
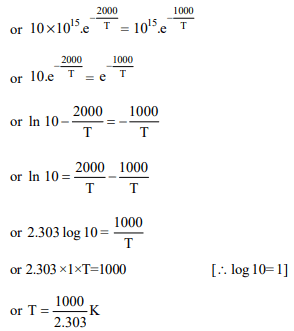
7. For the reaction, \[N_{2}+3H_{2}\rightarrow 2NH_{3}\]
\[\frac{d\left[NH_{3}\right]}{dt}=2 × 10^{-4} mol L^{-1} s^{-1},\]
the value of \[\frac{-d\left[H_{2}\right]}{dt}\] would be :
a) \[4 × 10^{-4} mol L^{-1} s^{-1}\]
b) \[6 × 10^{-4} mol L^{-1} s^{-1}\]
c) \[1 × 10^{-4} mol L^{-1} s^{-1}\]
d) \[3 × 10^{-4} mol L^{-1} s^{-1}\]
Explanation:
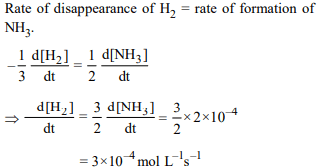
8. In the reaction
\[BrO_3^-\left(aq\right)+5Br^{-}\left(aq\right)+6H^{+}\left(aq\right)\rightarrow 3Br_{2}\left(l\right)+3H_{2}O\left(l\right)\]
The rate of appearance of bromine (Br2) is related to rate of
disappearance of bromide ions as following
a) \[\frac{d\left[Br_{2}\right]}{dt}=-\frac{5}{3}\frac{d\left[Br^{-}\right]}{dt}\]
b) \[\frac{d\left[Br_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{5}{3}\frac{d\left[Br^{-}\right]}{dt}\]
c) \[\frac{d\left[Br_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{3}{5}\frac{d\left[Br^{-}\right]}{dt}\]
d) \[\frac{d\left[Br_{2}\right]}{dt}=-\frac{3}{5}\frac{d\left[Br^{-}\right]}{dt}\]
Explanation:
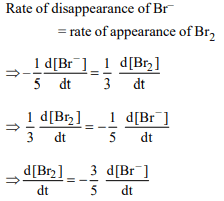
9.Half life period of a first-order reaction is 1386 seconds. The
specific rate constant of the reaction is :
a) \[0.5 × 10^{-2} S^{-1}\]
b) \[0.5 × 10^{-3} S^{-1}\]
c) \[5.0 × 10^{-2} S^{-1}\]
d) \[5.0 × 10^{-3} S^{-1}\]
Explanation:
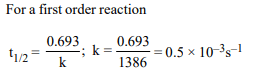
10. For the reaction \[A+B\rightarrow\] products, it is observed that:
(1) On doubling the initial concentration of A only, the rate
of reaction is also doubled and
(2) On doubling the initial concentrations of both A and B,
there is a change by a factor of 8 in the rate of the reaction.
The rate of this reaction is given by
a) \[rate = k \left[A\right] \left[B\right]^{2}\]
b) \[rate = k \left[A\right]^{2} \left[B\right]^{2}\]
c) \[rate = k \left[A\right] \left[B\right]\]
d) \[rate = k \left[A\right]^{2} \left[B\right]\]
Explanation:
