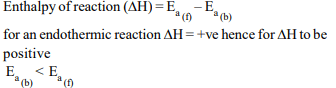1. Units of rate constant of first and zero order reactions in
terms of molarity (M) unit are respectively,
a) \[sec^{-1}, Msec^{-1}\]
b) \[sec^{-1}, M\]
c) \[Msec^{-1}, sec^{-1}\]
d) \[M, sec^{-1}\]
Explanation:
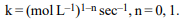
2.For the reaction \[A+2B\rightarrow C\] , rate is given by \[R=\left[A\right]\left[B\right]^{2}\] then the order of the reaction is
a) 3
b) 6
c) 5
d) 7
Explanation: Order is the sum of the power of the concentrations terms in rate law expression.
Order of reaction = 1+2 = 3
3. The differential rate law for the reaction
\[H_{2}+I_{2}\rightarrow 2HI\] is
a) \[-\frac{d\left[H_{2}\right]}{dt}=-\frac{d\left[I_{2}\right]}{dt}=-\frac{d\left[HI\right]}{dt}\]
b) \[\frac{d\left[H_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{d\left[I_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{1}{2}\frac{d\left[HI\right]}{dt}\]
c) \[\frac{1}{2}\frac{d\left[H_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{1}{2} \frac{d\left[I_{2}\right]}{dt}=-\frac{d\left[HI\right]}{dt}\]
d) \[-2\frac{d\left[H_{2}\right]}{dt}=-2 \frac{d\left[I_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{d\left[HI\right]}{dt}\]
Explanation: \[-2\frac{d\left[H_{2}\right]}{dt}=-2 \frac{d\left[I_{2}\right]}{dt}=\frac{d\left[HI\right]}{dt}\]
4.The integrated rate equation is
\[Rt = log C_{0} - logC_{t}\]
The straight line graph is obtained by plotting
a) time Vs log \[C_{t}\]
b) \[\frac{1}{time}\] Vs \[C_{t}\]
c) time Vs \[C_{t}\]
d) \[\frac{1}{time}\] Vs \[\frac{1}{C_{t}}\]
Explanation: time Vs log \[C_{t}\]
5. In respect of the equation \[k = Ae^{-E_{a} / RT}\] in chemical kinetics,
which one of the following statements is correct ?
a) A is adsorption factor
b) \[E_{a}\] is energy of activation
c) R is Rydberg’s constant
d) k is equilibrium constant
Explanation:
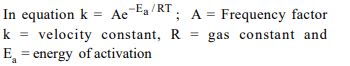
6. The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and B
is given by
\[Rate = k \left[A\right]^{n} \left[B\right]^{m}\]
On doubling the concentration of A and halving the
concentration of B, the ratio of the new rate to the earlier rate
of the reaction will be as
a) (m + n)
b) (n – m)
c) \[2^{(n – m)}\]
d) \[\frac{1}{2^{(m + n)}}\]
Explanation:
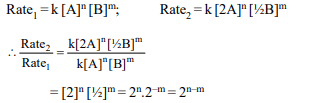
7. For the reaction system :
\[2NO\left(g\right)+O_{2}\left(g\right)\rightarrow 2NO_{2}\left(g\right)\]
volume is suddenly reduced
to half its value by increasing the pressure on it. If the reaction
is of first order with respect to \[O_{2}\] and second order with
respect to NO, the rate of reaction will
a) diminish to one-eighth of its initial value,
b) increase to eight times of its initial value
c) increase to four times of its initial value
d) diminish to one-fourth of its initial value
Explanation:
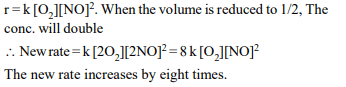
8. In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant,
decreases from 0.8 M to 0.4 M in 15 minutes. The time taken
for the concentration to change from 0.1 M to 0.025 M is
a) 7.5 minutes
b) 15 minutes
c) 30 minutes
d) 60 minutes
Explanation:
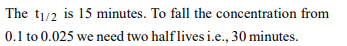
9. The rate equation for the reaction \[2A + B \rightarrow C\] is found to
be : rate = k[A][B]. The correct statement in relation to this
reaction is that the
a) rate of formation of C is twice the rate of disappearance
of A
b) \[t_{1/2}\] is a constant
c) unit of k must be \[s^{-1}\]
d) value of k is independent of the initial concentrations of
A and B
Explanation: The velocity constant depends on temperature only. It is independent of concentration of reactants
10. Consider an endothermic reaction \[X\rightarrow Y\] with the activation
energies \[E_{b}\] and \[E_{f}\] for the backward and forward reactions,
respectively. In general
a) there is no definite relation between \[E_{b}\] and \[E_{f}\]
b) \[E_{b}= E_{f}\]
c) \[E_{b}> E_{f}\]
d) \[E_{b}< E_{f}\]
Explanation: