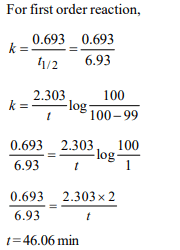1. A reaction involving two different reactants can never be
a) bimolecular reaction
b) second order reaction
c) first order reaction
d) unimolecular reaction
Explanation: The molecularity of a reaction is the number of reactant molecules taking part in a single step of the reaction. Thus the reaction involving two different reactant can never be unimolecular.
2. \[t_{1/4}\] can be taken as the time taken for the concentration of a
reactant to drop to\[\frac{3}{4}\]of its initial value. If the rate constant
for a first order reaction is K, the \[t_{1/4}\] can be written as
a) 0.75/k
b) 0.69/k
c) 0.29/k
d) 0.10/k
Explanation:
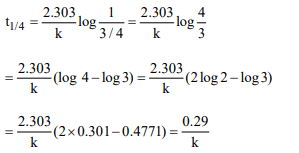
3. A reaction was found to be second order with respect to the
concentration of carbon monoxide. If the concentration of
carbon monoxide is doubled, with everything else kept the
same, the rate of reaction will
a) increase by a factor of 4
b) double
c) remain unchanged
d) triple
Explanation:

4. Rate of a reaction can be expressed by Arrhenius equation
as : \[k = A e^{–E/RT}\]
In this equation, E represents
a) the total energy of the reacting molecules at a
temperature, T
b) the fraction of molecules with energy greater than the
activation energy of the reaction
c) the energy above which all the colliding molecules will
react
d) the energy below which colliding molecules will not
react
Explanation:
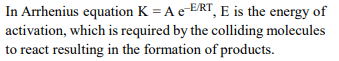
5.The following mechanism has been proposed for the
reaction of NO with Br2 to form NOBr:
\[NO\left(g\right) + Br_{2}\left(g\right)\rightleftharpoons NOBr_{2}\left(g\right)\]
\[NOBr_{2}\left(g\right) + NO\left(g\right)\rightarrow 2NOBr\left(g\right)\]
If the second step is the rate determining step, the order of
the reaction with respect to \[ NO\left(g\right)\] is
a) 3
b) 2
c) 1
d) 0
Explanation:
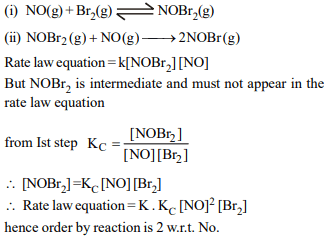
6. The energies of activation for forward and reverse reactions
for \[A_{2}+B_{2}\rightleftharpoons2AB\] are 180 kJ \[mol^{-1}\] and 200 kJ \[mol^{-1}\]
respectively. The presence of a catalyst lowers the activation
energy of both (forward and reverse) reactions by 100 kJ \[mol^{-1}\] . The enthalpy change of the reaction \[\left(A_{2}+B_{2}\rightarrow2AB\right)\]
in the presence of a catalyst will be (in kJ \[mol^{-1})\]
a) 20
b) 300
c) 120
d) 280
Explanation:
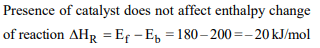
7. Consider the reaction, \[2A+B\rightarrow\] products. When
concentration of B alone was doubled, the half-life did not
change. When the concentration of A alone was doubled, the
rate increased by two times. The unit of rate constant for this
reaction is
a) \[s^{-1}\]
b) L \[mol^{-1} s^{-1}\]
c) no unit
d) mol \[L^{-1} s^{-1}\]
Explanation:

8.A radioactive element gets spilled over the floor of a room. Its
half-life period is 30 days. If the initial velocity is ten times the
permissible value, after how many days will it be safe to enter
the room?
a) 100 days
b) 1000 days
c) 300 days
d) 10 days
Explanation:
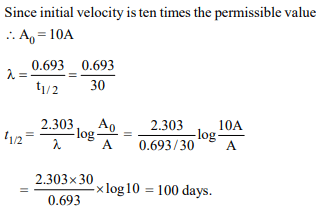
9. For a reaction\[\frac{1}{2}A\rightarrow 2B\] rate of disappearance of ‘A’ is
related to the rate of appearance of ‘B’ by the expression
a) \[-\frac{d\left[A\right]}{dt}=\frac{1}{2}\frac{d\left[B\right]}{dt}\]
b) \[-\frac{d\left[A\right]}{dt}=\frac{1}{4}\frac{d\left[B\right]}{dt}\]
c) \[-\frac{d\left[A\right]}{dt}=\frac{d\left[B\right]}{dt}\]
d) \[-\frac{d\left[A\right]}{dt}=4\frac{d\left[B\right]}{dt}\]
Explanation:
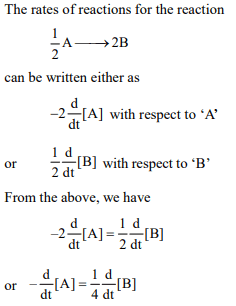
10. The half life period of a first order chemical reaction is 6.93
minutes. The time required for the completion of 99% of the
chemical reaction will be (log 2 = 0.301)
a) 23.03 minutes
b) 46.06 minutes
c) 460.6 minutes
d) 230.03 minutes
Explanation: