1. The decomposition of a substance follows first order kinetics.
Its concentration is reduced to 1/8th of its initial value in 24
minutes. The rate constant of the decomposition process is
a)\[1/24 min^{-1}\]
b) \[\frac{0.692}{24} min^{-1}\]
c) \[\frac{2.303}{24}log\frac{1}{8} min^{-1}\]
d) \[\frac{2.303}{24}log\frac{8}{1} min^{-1}\]
Explanation:
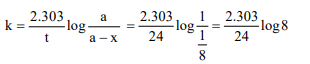
2. The rate of chemical reaction is doubled for every 10°C rise
in temperature because of
a) increase in the activation energy
b) decrease in the activation energy
c) increase in the number of molecular collisions
d) increase in the number of activated molecules
Explanation: With temperature the number of activated molecules increase
3. The temperature coefficient of most of the reactions lies
between
a) 1 and 3
b) 2 and 3
c) 1 and 4
d) 2 and 4
Explanation: Between 2 and 3
4. The velocity of a reaction is doubled for every 10°C rise in
temp. If the temp. is raised to 50°C the reaction velocity
increases by about
a) 12 times
b) 16 times
c) 32 times
d) 50 times
Explanation:

5. For the reaction \[A\rightarrow B\] , the rate law expression is : rate
= k [A]. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a) The reaction follows first order kinetics
b) The \[t_{1/2}\] of reaction depends on initial concentration of
reactants
c) k is constant for the reaction at a constant temperature
d) The rate law provides a simple way of predicting the
conc. of reactants and products at any time after the
start of the reaction
Explanation:
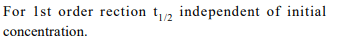
6. For a reaction of type \[A+B\rightarrow\] products , it is observed
that doubling concentration of A causes the reaction rate to
be four times, but doubling amount of B does not affect the
rate. The rate equation is
a) Rate = k [A] [B]
b) \[Rate = \frac{K}{4}\left[A\right]^{2}\]
c) \[Rate = k \left[A\right]^{2} \left[B\right]\]
d) \[Rate = k \left[A\right]^{2} \left[B\right]^{2}\]
Explanation:
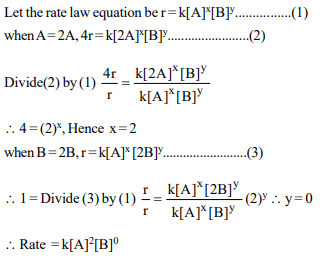
7. The chemical reaction \[2O_{3}\rightarrow 3O_{2}\] proceeds as follows
:\[O_{3}\rightarrow O_{2}+O;O+O_{3}\rightarrow 2O_{2}\]
the rate law
expression should be
a) \[r = k\left[O_{3}\right]^{2}\]
b) \[r = k\left[O_{3}\right]^{2}\left[O_{2}\right]^{-1}\]
c) \[r = k^{3}\left[O_{3}\right]\left[O_{2}\right]^{2}\]
d) \[r = \left[O_{3}\right]\left[O_{2}\right]^{2}\]
Explanation:
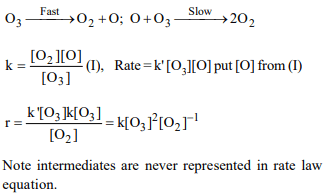
8. For the reaction \[2H_{2}O_{2}\rightarrow 2H_{2}O+O_{2} , r= K \left[H_{2}O_{2}\right]\]
It
is
a) zero order reaction
b) first order reaction
c) second order reaction
d) third order reaction
Explanation: 1st order reaction
9. If the rate of the reaction is equal to the rate constant, the
order of the reaction is
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 0
Explanation:

10. For the reaction \[A+B\rightarrow C\] , it is found that doubling
the concentration of A increases the rate 4 times, and
doubling the concentration of B doubles the reaction rate.
What is the overall order of the reaction?
a) \[3/2\]
b) 4
c) 1
d) 3
Explanation: Order with respect to A is 2 and B is 1
Order of reaction = 2+1 = 3