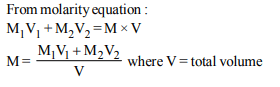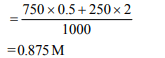1. A 5.25% solution of a substance is isotonic with a 1.5% solution
of urea (molar mass = 60 g \[mol^{-1})\] in the same solvent. If the
densities of both the solutions are assumed to be equal to
1.0 g \[cm^{-3}\] , molar mass of the substance will be
a) 210.0 g \[mol^{-1}\]
b) 90.0 g \[mol^{-1}\]
c) 115.0 g \[mol^{-1}\]
d) 105.0 g \[mol^{-1}\]
Explanation:
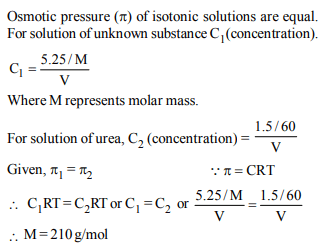
2. At 80° C, the vapour pressure of pure liquid ‘A’ is 520 mm Hg
and that of pure liquid ‘B’ is 1000 mm Hg. If a mixture solution
of ‘A’ and ‘B’ boils at 80° C and 1 atm pressure, the amount of
‘A’ in the mixture is (1 atm = 760 mm Hg)
a) 52 mol percent
b) 34 mol percent
c) 48 mol percent
d) 50 mol percent
Explanation:
3. The vapour pressure of water at 20°C is 17.5 mm Hg. If 18 g of
glucose \[\left(C_{6}H_{12}O_{6}\right)\] is added to 178.2 g of water at 20°C, the
vapour pressure of the resulting solution will be
a) 17.325 mm Hg
b) 15.750 mm Hg
c) 16.500 mm Hg
d) 17.500 mm Hg
Explanation:
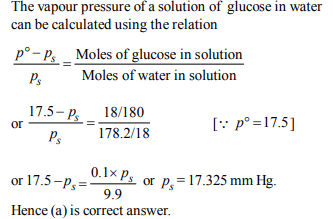
4. A binary liquid solution is prepared by mixing n-heptane and
ethanol. Which one of the following statements is correct
regarding the behaviour of the solution?
a) The solution is non-ideal, showing – ve deviation from
Raoult’s Law
b) The solution is non-ideal, showing + ve deviation from
Raoult’s Law.
c) n-heptane shows + ve deviation while ethanol shows
– ve deviation from Raoult’s Law.
d) The solution formed is an ideal solution
Explanation: For this solution intermolecular interactions between n-heptane and ethanol are weaker than n-heptane-nheptane & ethanol-ethanol interactions hence the solution of n-heptane and ethanol is non-ideal and shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law
5.Two liquids X and Y form an ideal solution. At 300 K, vapour
pressure of the solution containing 1 mol of X and 3 mol of Y
is 550 mm Hg. At the same temperature, if 1 mol of Y is further
added to this solution, vapour pressure of the solution
increases by 10 mm Hg. Vapour pressure ( in mm Hg) of X and
Y in their pure states will be, respectively:
a) 300 and 400
b) 400 and 600
c) 500 and 600
d) 200 and 300
Explanation:
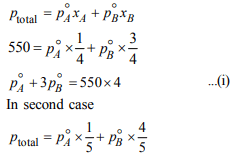
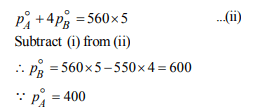
6. If sodium sulphate is considered to be completely dissociated
into cations and anions in aqueous solution, the change in
freezing point of water \[\left(\triangle T_{f}\right)\] , when 0.01 mol
of sodium sulphate is dissolved in 1 kg of water, is \[(K_{f}\] =1.86K kg \[mol^{-1})\]
a) 0.372 K
b)0.0558 K
c) 0.0744 K
d) 0.0186 K
Explanation:
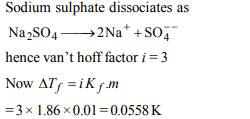
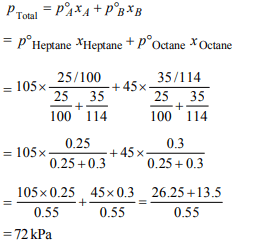
7. On mixing, heptane and octane form an ideal solution. At
373 K, the vapour pressures of the two liquid components
(heptane and octane) are 105 kPa and 45 kPa respectively.
Vapour pressure of the solution obtained by mixing 25.0 g of
heptane and 35 g of octane will be (molar mass of heptane=100 g \[mol^{-1}\] and of octane = 114 g \[mol^{-1})\]
a) 72.0 kPa
b) 36.1 kPa
c) 96.2 kPa
d) 144.5 kPa
Explanation:
8. A 5% solution of cane sugar (molar mass 342) is isotonic with
1% of a solution of an unknown solute. The molar mass of
unknown solute in g/mol is :
a) 171.2
b) 68.4
c) 34.2
d) 136.2
Explanation:
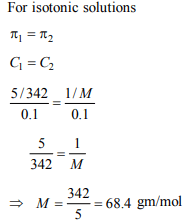
9. \[K_{f}\] for water is 1.86 K kg \[mol^{-1}\] . If your automobile radiator
holds 1.0 kg of water, how many grams of ethylene glycol
\[\left(C_{2}H_{6}O_{2}\right)\] must you add to get the freezing point of the
solution lowered to –2.8ºC ?
a) 72 g
b) 93 g
c) 39 g
d) 27 g
Explanation:
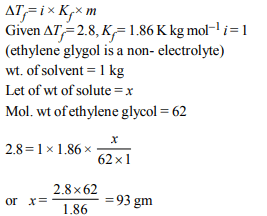
10. The molarity of a solution obtained by mixing 750 mL of 0.5(M)
HCl with 250 mL of 2(M) HCl will be :
a) 0.875 M
b) 1.00 M
c) 1.75 M
d) 0.975 M
Explanation: