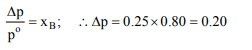1.An aqueous solution of 6.3 g oxalic acid dihydrate is made
upto 250 ml. The volume of 0.1 N NaOH required to completely
neutralize 10 ml of this solution is
a) 40 ml
b) 20 ml
c) 10 ml
d) 4 ml
Explanation:
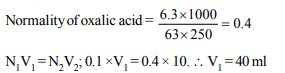
2. 2.5 litre of 1 M NaOH solution are mixed with another 3 litre
of 0.5 M NaOH solution. Then the molarity of the resulting
solution is
a) 0.80 M
b) 1.0 M
c) 0.73 M
d) 0.50 M
Explanation:
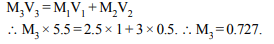
3.12g of urea is dissolved in 1 litre of water and 68.4 g of
sucrose is dissolved in 1 litre of water. The lowering of vapour
pressure of first case is
a) equal to second
b) greater than second
c) less than second
d) double that of second
Explanation:
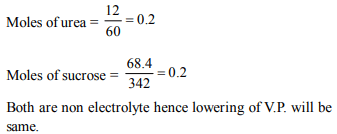
4. Which of the following statement is correct if the
intermolecular forces in liquids A, B and C are in the order
A < B < C?
a) B evaporates more readily than A
b) B evaporates less readily than C
c) A and B evaporates at the same rate
d) A evaporates more readily than C
Explanation: Lesser the intermolecular forces, the more the volatile character.
5.The aqueous solution that has the lowest vapour pressure
at a given temperature is
a) 0.1 molal sodium phosphate
b) 0.1 molal barium chloride
c) 0.1 molal glucose
d) 0.1 molal acetic acid
Explanation:
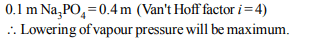
6. Vapour pressure of \[CCl_{4}\] at 25°C is 143 mm Hg. 0.5 g of a nonvolatile
solute (mol. wt. 65) is dissolved in 100 ml of \[CCl_{4}\] .
Find the vapour pressure of the solution. (Density of \[CCl_{4}\] =1.58 \[g/cm^{3})\]
a) 141.93 mm Hg
b) 94.39 mm Hg
c) 199.34 mm Hg
d) 143.99 mm Hg
Explanation:
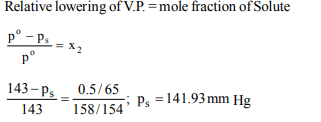
7.The vapour pressure of solvent decreases by 10 mm of
mercury when a non-volatile solute was added to the solvent.
The mole fraction of the solute in the solution is 0.2. What
should be the mole fraction of the solvent if the decrease in
vapour pressure is to be 20 mm of mercury ?
a) 0.8
b) 0.6
c) 0.4
d) 0.2
Explanation:
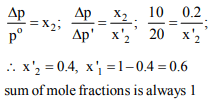
8. The vapour pressure of a solvent A is 0.80 atm. When a nonvolatile
substance B is added to this solvent its vapour
pressure drops to 0.6 atm. the mole fraction of B in the solution
is
a) 0.25
b) 0.50
c) 0.75
d) 0.90
Explanation:
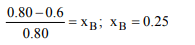
9. At a particular temperature, the vapour pressures of two
liquids A and B are respectively 120 and 180 mm of mercury.
If 2 moles of A and 3 moles of B are mixed to form an ideal
solution, the vapour pressure of the solution at the same
temperature will be (in mm of mercury)
a) 156
b) 145
c) 150
d) 108
Explanation:
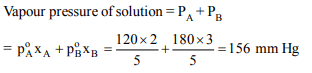
10. At room temperature, the mole fraction of a solute is 0.25 and
the vapour pressure of a solvent is 0.80 atm. Then the lowering
of vapour pressure is
a) 0.75
b) 0.60
c) 0.20
d) 0.80
Explanation: