1.At 30°C and 40°C the vapour pressure of a liquid are 0.025
and 0.050 atm respectively. Calculate the heat of vaporization
of the liquid
a) 14.06 cal/mol
b) 13060 cal/mol
c) 140.8 cal /mol
d) 2160 cal/ mol
Explanation:
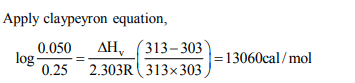
2. The equilibrium vapour pressure of water vapour over a 0.20
mole sample of water (l) is 35 torr at 27°C. If the amount of the
liquid water is decreased to 0.10 mole, the equilibrium vapour
pressure of it would be
a) 17.5 torr
b) 35.0 torr
c) 51.5 torr
d) None of these
Explanation: The equilibrium vapour pressure will remain the same. It is independent of the quantity of substance
3. A flask is partially evacuated to 400 torr pressure of air. A
small amount of benzene is introduced into the flask in order
that some liquid will remain after equilibrium has been
established. The vapour pressure of benzene at 25°C is 220
torr. What is the total pressure in the flask at equilibrium at
25°C ?
a) 120 torr
b) 510 torr
c) 620 torr
d) 480 torr
Explanation: The total pressure will be the sum of pressures of air and benzene
4. Which of the following solutions will have the highest
boiling point?
a) 0.5 molal \[BaCl_{2}\]
b) 1.0 molal KBr
c) \[1.8 × 10^{24}\] glucose molecules per litre.
d) 100 g powdered glucose in one litre water
Explanation:
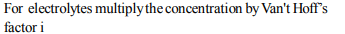
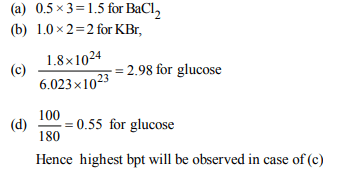
5. Two 1-litre flask A and B are connected to each other by a
valve which is closed. Flask A has benzene in equilibrium
with its vapours at 30°C. The flask B, is evacuated, and the
valve is opened. Which of the following is true. If temperature
is kept constant.’
a) Some of the benzene molecules would move to flask B
from flask A.
b) Vapour pressure will be half the initial value
c) The vapour pressure remains unchanged
d) Some more of the liquid benzene in flask A would
evaporate.
Explanation: There is no change in vapour pressure.
6. The vapour pressure of ethanol and methanol are 42.0 mm
and 88.5 mm Hg respectively . An ideal solution is formed at
the same temperature by mixing 46.0 g of ethanol with 16.0 g
of methanol. What is the mole fraction of methanol vapour ?
a)0.467
b) 0.502
c) 0.513
d) 0.556
Explanation:
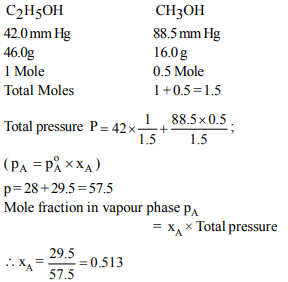
7. Which of the following solutions will have the maximum
lowering of vapour pressure at 300 K
a) 1 \[M CaCl_{2}\]
b) 1 M NaCl
c) 1 M Phenol
d) 1 M sucrose
Explanation: Maximum lowering of vapour pressure will be given by the substance giving maximum number of particles in solution. In case of electrolytes do not forget. To multiply the molarity by Van’t Hoff factor i.
8. Two Aqueous solutions \[S_{1}\] and \[S_{2}\] are separated by a
semipermeable membrane . Solution \[S_{1}\] has got a greater
vapour pressure than solution \[S_{2}\] . Water will be flowing
a) from \[S_{1}\] to \[S_{2}\]
b) from \[S_{2}\] to \[S_{1}\]
c) in both the directions
d) in either direction depending upon the nature of the
solute
Explanation: In case of osmosis the flow of the solvent, from lower concentration to higher concentration
9. What is the degree of dissociation of sodium chloride, if the
molar mass determined by a cryoscopic method was found to
be 31.80 g \[mol^{-1}\] [Atomic mass Na = 23 g \[mol^{-1}\] Cl = 35.5 g \[mol^{-1}]\]
a) 0.58
b) 0.73
c) 0.84
d) 0.92
Explanation:

10. Consider the following statements
1. Isotonic solutions have the same molar concentration at
a given temperature
2. The molal elevation constant \[K_{b}\] is a characteristic of a
solvent, and is independent of the solute added
3. The freezing point of a 0.1 M aqueous KCl solution is
more than that of a 0.1 M aqueous \[AlCl_{3}\] solution.
Which of these statements is correct?
a) 1 and 2
b) 2 and 3
c) 1 and 3
d) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation: All the statements are correct