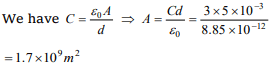1. The plates of a parallel plate capacitor of capacity 50 \[\mu C\]
are charged to a potential of 100 volts and then separated
from each other so that the distance between them is
doubled. How much is the energy spent in doing so
a) \[25\times 10^{-2}J\]
b) \[-12.5\times 10^{-2}J\]
c) \[-25\times 10^{-2}J\]
d) \[12.5\times 10^{-2}J\]
Explanation:
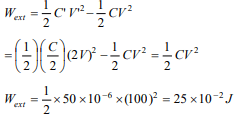
2. Two spherical conductors each of capacity C are charged
to potentials V and -V . These are then connected by
means of a fine wire. The loss of energy will be
a) Zero
b) \[\frac{1}{2}CV^{2}\]
c) \[CV^{2}\]
d) \[2CV^{2}\]
Explanation:
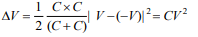
3.The area of the plates of a parallel plate condenser is A and
the distance between the plates is 10 mm . There are two
dielectric sheets in it, one of dielectric constant 10 and
thickness 6 mm and the other of dielectric constant 5 and
thickness 4 mm . The capacity of the condenser is
a) \[\frac{12}{35}\epsilon_{0}A\]
b) \[\frac{2}{3}\epsilon_{0}A\]
c) \[\frac{5000}{7}\epsilon_{0}A\]
d) \[1500\epsilon_{0}A\]
Explanation:
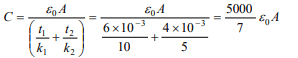
4. An air capacitor of capacity \[C=10\mu F\] is connected to a
constant voltage battery of 12 V . Now the space between
the plates is filled with a liquid of dielectric constant 5. The
charge that flows now from battery to the capacitor is
a) 120 \[\mu C\]
b) 699 \[\mu C\]
c) 480 \[\mu C\]
d) 24 \[\mu C\]
Explanation: Initially charge on the capacitor
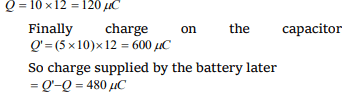
5. A parallel plate capacitor is first charged and then a
dielectric slab is introduced between the plates. The
quantity that remains unchanged is
a) Charge Q
b) Potential V
c) Capacity C
d) Energy U
Explanation: Charge Q
6. A \[2\mu F\] capacitor is charged to 100 volt and then its plates
are connected by a conducting wire. The heat produced is
a) 1 J
b) 0.1 J
c) 0.01 J
d) 0.001 J
Explanation: Heat produced = Energy of charged capacitor
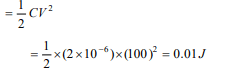
7. The force between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor of
capacitance C and distance of separation of the plates d
with a potential difference V between the plates, is
a) \[\frac{CV^{2}}{2d}\]
b) \[\frac{C^{2}V^{2}}{2d^{2}}\]
c) \[\frac{C^{2}V^{2}}{d^{2}}\]
d) \[\frac{V^{2}d}{C}\]
Explanation: \[\frac{CV^{2}}{2d}\]
8. Two metal spheres of capacitance C1 and C2 carry some
charges. They are put in contact and then separated. The
final charges \[Q_{1}\] and \[Q_{2}\] on them will satisfy
a) \[\frac{Q_{1}}{Q_{2}}<\frac{C_{1}}{C_{2}}\]
b) \[\frac{Q_{1}}{Q_{2}}=\frac{C_{1}}{C_{2}}\]
c) \[\frac{Q_{1}}{Q_{2}}>\frac{C_{1}}{C_{2}}\]
d) \[\frac{Q_{1}}{Q_{2}}<\frac{C_{2}}{C_{1}}\]
Explanation: Potential of both spheres will be same.
9. A parallel plate condenser with oil between the plates
(dielectric constant of oil k=2) has a capacitance C . If the
oil is removed, then capacitance of the capacitor becomes
a) \[\sqrt{2 }C\]
b) 2C
c) \[\frac{C}{\sqrt{2 }}\]
d) \[\frac{C}{2}\]
Explanation:
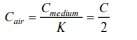
10. What is the area of the plates of a 3F parallel plate
capacitor, if the separation between the plates is 5mm
a) \[1.694 \times10^{9}m^{2}\]
b) \[4.529 \times10^{9}m^{2}\]
c) \[9.281\times10^{9}m^{2}\]
d) \[12.981 \times10^{9}m^{2}\]
Explanation: