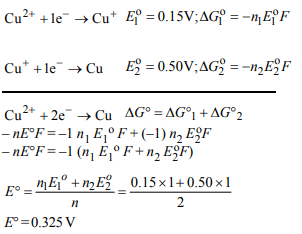1. Standard free energies of formation (in kJ/mol) at 298 K are
– 237.2, – 394.4 and – 8.2 for \[H_{2}O\left(l\right), CO_{2}\left(g\right)\] and pentane (g),
respectively. The value E°cell for the pentane-oxygen fuel cell
a) 1.968 V
b) 2.0968 V
c) 1.0968 V
d) 0.0968 V
Explanation:

2. Given:
(i) \[Cu^{2+}+2e^{-}\rightarrow Cu, E^{\circ} = 0.337 V\]
(ii) \[Cu^{2+}+e^{-}\rightarrow Cu^{+}, E^{\circ} =0.153 V\]
Electrode potential, Eo for the reaction \[Cu^{+}+e^{-}\rightarrow Cu \] , will be :
a) 0.90 V
b) 0.30 V
c) 0.38 V
d) 0.52 V
Explanation:
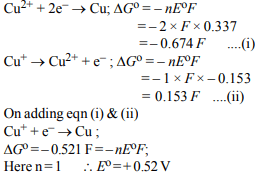
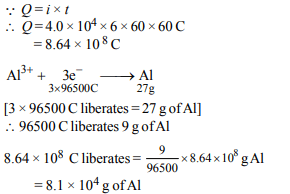
3. \[Al_{2}O_{3}\] is reduced by electrolysis at low potentials and high
currents. If \[4.0 × 10^{4}\] amperes of current is passed through
molten \[Al_{2}O_{3}\] for 6 hours, what mass of aluminium is
produced? (Assume 100% current efficiency. At. mass of Al= 27 g \[mol^{-1})\]
a) \[8.1 × 10 ^{4}g\]
b) \[2.4 × 10 ^{5}g\]
c) \[1.3 × 10 ^{4}g\]
d) \[9.0 × 10 ^{3}g\]
Explanation:
4. The equivalent conductance of \[\frac{M}{32}\] solution of a weak
monobasic acid is 8.0 mho cm2 and at infinite dilution is 400 mho \[cm ^{2}\] . The dissociation constant of this acid is:
a) \[1.25 × 10 ^{-6}\]
b) \[6.25 × 10 ^{-4}\]
c) \[1.25 × 10 ^{-4}\]
d) \[1.25 × 10 ^{-5}\]
Explanation:
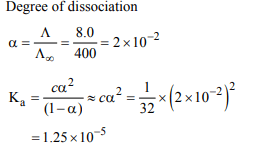
5.For the reduction of silver ions with copper metal, the standard
cell potential was found to be + 0.46 V at 25°C.
The value of standard Gibbs energy, \[\triangle G^{\circ}\] will be (F = 96500 C \[mol^{-1})\]
a) – 89.0 kJ
b) – 89.0 J
c) – 44.5 kJ
d) – 98.0 kJ
Explanation:
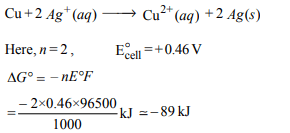
6. An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte
with dilution is mainly due to:
a) increase in ionic mobility of ions
b) 100% ionisation of electrolyte at normal dilution
c) increase in both i.e. number of ions and ionic mobility of
ions
d) increase in number of ions
Explanation:

7. Which of the following expressions correctly represents the
equivalent conductance at infinite dilution of \[Al_{2}\left(SO_{4}\right)_{3}\] ,
Given that \[\wedge^{\circ}_{Al^{3+}}\] and \[\wedge^{\circ}_{SO_4^{2-}}\] are the equivalent
conductances at infinite dilution of the respective ions?
a) \[\frac{1}{3}\wedge^{\circ}_{Al^{3+}}+\frac{1}{2}\wedge^{\circ}_{SO_4^{2-}}\]
b) \[2\wedge^{\circ}_{Al^{3+}}+3\wedge^{\circ}_{SO_4^{2-}}\]
c) \[\wedge^{\circ}_{Al^{3+}}+\wedge^{\circ}_{SO_4^{2-}}\]
d) \[\left(\wedge^{\circ}_{Al^{3+}}+\wedge^{\circ}_{SO_4^{2-}}\right)\times 6\]
Explanation:

8. Consider the following relations for emf of a electrochemical
cell:
(i) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) –
(Reduction potential of cathode)
(ii) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) + (Reduction
potential of cathode)
(iii) emf of cell = (Reduction potential of anode) + (Reduction
potential of cathode)
(iv) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Oxidation
potential of cathode)
Which of the above relations are correct?
a) (ii) and (iv)
b) (iii) and (i)
c) (i) and (ii)
d) (iii) and (iv)
Explanation:
9. Standard electrode potential of three metals X, Y and Z are
– 1.2 V, + 0.5 V and – 3.0 V, respectively. The reducing power
of these metals will be :
a) Y > Z > X
b) X > Y > Z
c) Z > X > Y
d) X > Z > Y
Explanation:
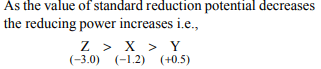
10.The electrode potentials for
\[Cu^{2+}\left(aq\right)+e^{-}\rightarrow Cu^{+}\left(aq\right)\]
and \[Cu^{+}\left(aq\right)+e^{-}\rightarrow Cu\left(s\right)\]
are + 0.15 V and + 0.50, respectively. The value of
\[E^{\circ}_{Cu^{2+}/Cu}\] will be :
a) 0.500 V
b) 0.325 V
c) 0.650 V
d) 0.150 V
Explanation: