1. The thermodynamic efficiency of cell is given by
a) \[\triangle H/\triangle G\]
b) \[nFE/\triangle G\]
c) \[nFE/\triangle H\]
d) nFE
Explanation:

2. The electroplating with chromium is undertaken because
a) electrolysis of chromium is easier
b) chromium can form alloys with other metals
c) chromium gives protective and decorative coating to
the base metal
d) of the high reactivity of metallic chormium
Explanation: chromium gives protective and decorative coating to the base metal
3. Prevention of corrosion of iron by Zn coating is called
a) galvanization
b) cathodic protection
c) electrolysis
d) photoelectrolysis
Explanation:

4. Which of the following statements is correct?
a) Oxidation number of oxygen in \[KO_{2}\] is +1
b) The specific conductance of an electrolyte solution
decreases with increase in dilution
c) \[Sn^{2+}\] oxidises \[Fe^{3+}\]
d) \[Zn/ZnSO_{4}\] is a reference electrode
Explanation:
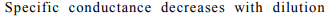
5.In the electrolytic cell, flow of electrons is from
a) cathode to anode in solution
b) cathode to anode through external supply
c) cathode to anode through internal supply
d) anode to cathode through internal supply
Explanation:

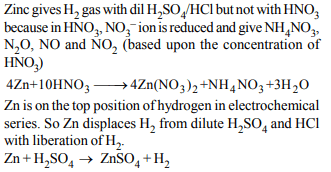
6. Zn gives \[H_{2}\] gas with \[H_{2}SO _{4}\] and HCl but not with \[HNO _{3}\] because
a) Zn acts as an oxidising agent when it reacts with \[HNO _{3}\]
b) \[HNO _{3}\] is weaker acid than \[H_{2}SO _{4}\] and HCl
c) in electrochemical series, Zn is above hydrogen
d) \[NO_3^-\] is reduced in preference to hydronium ion
Explanation:
7. The efficiency of a fuel cell is given by
a) \[\frac{\triangle G}{\triangle S}\]
b) \[\frac{\triangle G}{\triangle H}\]
c) \[\frac{\triangle S}{\triangle G}\]
d) \[\frac{\triangle H}{\triangle G}\]
Explanation:
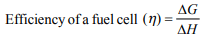
8. The equilibrium constant of the reaction:
\[Cu \left(s\right)+2Ag^{+}\left(aq\right)\rightleftharpoons Cu^{2+}(aq)+2Ag \left(s\right);E° = 0.46 V\]
at 298 K is
a) \[2.0 × 10^{10}\]
b) \[4.0 × 10^{10}\]
c) \[4.0 × 10^{15}\]
d) \[2.4 × 10^{10}\]
Explanation:
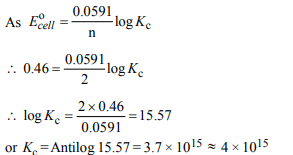
9. On the basis of the following E° values, the strongest oxidizing
agent is :
\[\left[Fe\left( CN\right)_{6}\right]^{4-}\rightarrow\left[Fe\left( CN\right)_{6}\right]^{3-}+e^{-};E° = – 0.35 V\]
\[Fe^{2+}\rightarrow Fe^{3+} +e^{-};E° = – 0.77 V\]
a) \[\left[Fe\left( CN\right)_{6}\right]^{4-}\]
b) \[Fe^{2+}\]
c) \[Fe^{3+}\]
d) \[\left[Fe\left( CN\right)_{6}\right]^{3-}\]
Explanation:

10. Kohlrausch’s law states that at :
a) finite dilution, each ion makes definite contribution to
equivalent conductance of an electrolyte, whatever be
the nature of the other ion of the electrolyte.
b) infinite dilution each ion makes definite contribution to
equivalent conductance of an electrolyte depending on
the nature of the other ion of the electrolyte
c) infinite dilution, each ion makes definite contribution to
conductance of an electrolyte whatever be the nature of
the other ion of the electrolyte
d) infinite dilution, each ion makes definite contribution to
equivalent conductance of an electrolyte, whatever be
the nature of the other ion of the electrolyte.
Explanation:
