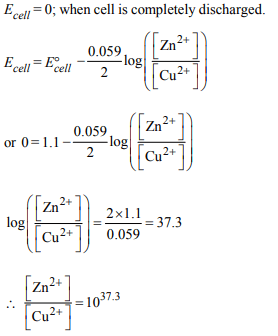1.Consider the following Eº values
\[E^{\circ}_{Fe^{3+}/Fe^{2+}}=+0.77 V ;E^{\circ}_{Sn^{2+}/Sn}=-0.14 V\]
Under standard conditions the potential for the reaction
\[Sn\left(s\right)+2Fe^{3+}\left(aq\right)\rightarrow2Fe^{2+}\left(aq\right)+Sn^{2+}\left(aq\right)\]
is
a) 0.91 V
b) 1.40 V
c) 1.68 V
d) 0.63 V
Explanation:
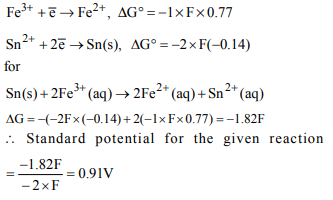
2. The standard e.m.f. of a cell involving one electron change
is found to be 0.591 V at 25ºC. The equilibrium constant of
the reaction will be
\[\left(F = 96,500 C moI^{-1};R = 8.314 JK^{-1}moI^{-1}\right)\]
a) \[1.0 × 10^{10}\]
b) \[1.0 × 10^{5}\]
c) \[1.0 × 10^{1}\]
d) \[1.0 × 10^{30}\]
Explanation:
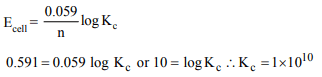
3. The limiting molar conductivities \[\wedge^{\circ}\] for NaCl, KBr and KCl
are 126, 152 and 150 S \[cm^{2} mol^{-1}\] respectively. The \[\wedge^{\circ}\] for
NaBr is
a) 278 S \[cm^{2} mol^{-1}\]
b) 176 S \[cm^{2} mol^{-1}\]
c) 128 S \[cm^{2} mol^{-1}\]
d) 302 S \[cm^{2} mol^{-1}\]
Explanation:
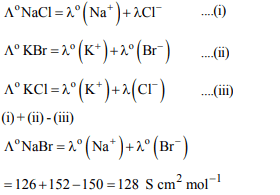
4. The \[E^{\circ}_{M^{3+}/M^{2+}}\] values for Cr, Mn, Fe and Co are – 0.41, +
1.57, + 0.77 and + 1.97V respectively. For which one of these
metals the change in oxidation state from +2 to +3 is easiest?
a) Fe
b) Mn
c) Cr
d) CO
Explanation:

5. The highest electrical conductivity of the following aqueous
solutions is of
a) 0.1 M difluoroacetic acid
b) 0.1 M fluoroacetic acid
c) 0.1 M chloroacetic acid
d) 0.1 M acetic acid
Explanation:
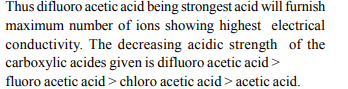
6. Aluminium oxide may be electrolysed at 1000°C
to furnish aluminium metal (At. Mass = 27 amu; 1 Faraday =
96,500 Coulombs). The cathode reaction is
\[Al^{3+}+3e^{-}\rightarrow Al\]
To prepare 5.12 kg of aluminium metal by this method we
require
a) \[5.49 × 10^{1}\] C of electricity
b) \[5.49 × 10^{4}\] C of electricity
c) \[1.83 × 10^{7}\] C of electricity
d) \[5.49 × 10^{7}\] C of electricity
Explanation:
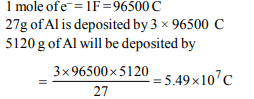
7. The molar conductivities \[\wedge^{\circ}_{NaOAc}\] and \[\wedge^{\circ}_{HCl}\] at infinite
dilution in water at 25ºC are 91.0 and 426.2 S \[cm^{2}/mol\]
respectively. To calculate \[\wedge^{\circ}_{HOAc}\] , the additional value
required is
a) \[\wedge^{\circ}_{NaOH}\]
b) \[\wedge^{\circ}_{NaCl}\]
c) \[\wedge^{\circ}_{H_{2}O}\]
d) \[\wedge^{\circ}_{KCl}\]
Explanation:

8. Resistance of a conductivity cell filled with a solution of an
electrolyte of concentration 0.1 M is 100 Ω . The conductivity
of this solution is 1.29 S \[m^{-1}\] . Resistance of the same cell
when filled with 0.2 M of the same solution is 520 Ω . The
molar conductivity of 0.02 M solution of electrolyte will be
a) 1.24 × \[10^{-4}\] S \[m^{2} mol^{-1}\]
b) 12.4 × \[10^{-4}\] S \[m^{2} mol^{-1}\]
c) 124 × \[10^{-4}\] S \[m^{2} mol^{-1}\]
d) 1240 × \[10^{-4}\] S \[m^{2} mol^{-1}\]
Explanation:
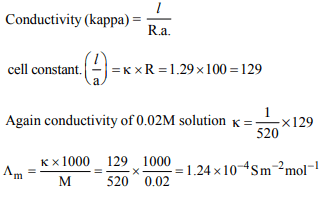
9. The equivalent conductances of two strong electrolytes at
infinite dilution in \[H_{2}O\] (where ions move freely through a
solution) at 25°C are given below :
\[\wedge^{\circ}_{CH_{3}COONa}\] = 91.0 S \[cm^{2}\] / equiv
\[\wedge^{\circ}_{HCl}\] = 426.2 S \[cm^{2}\] / equiv
What additional information/ quantity one needs to calculate
\[\wedge^{\circ}\] of an aqueous solution of acetic acid?
a) \[\wedge^{\circ}\] of chloroacetic acid \[\left({ClCH_{2}COOH}\right)\]
b) \[\wedge^{\circ}\] of NaCl
c) \[\wedge^{\circ}\] of \[{CH_{3}COOK}\]
d) the limiting equivalent coductance of \[H^{+}\left(\lambda^{\circ}_{H^{+}}\right)\]
Explanation:

10. The cell, \[Zn \mid Zn^{2+}\left(1 M\right)\parallel Cu^{2+}\left(1 M\right)\mid Cu \left(E^{\circ}_{cell}=1.10 V\right)\]
was allowed to be completely discharged at 298 K. The
relative concentration of \[Zn^{2+}\] to \[Cu^{2+}\left(\frac{\left[Zn^{2+}\right]}{\left[Cu^{2+}\right]}\right)\]
is
a) \[9.65 × 10^{4}\]
b) antilog (24.08)
c) 37.3
d) \[ 10^{37.3}\]
Explanation: