1.The ionization constant of ammonium hydroxide is \[1.77 × 10^{-5}\]
at 298 K. Hydrolysis constant of ammonium chloride is:
a) \[6.50 × 10^{-12}\]
b) \[5.65 × 10^{-13}\]
c) \[5.65 × 10^{-12}\]
d) \[5.65 × 10^{-10}\]
Explanation:
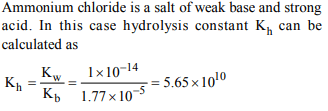
2. If pH of a saturated solution of \[Ba \left(OH\right)_{2}\] is 12, the value of
its \[K_\left({sp}\right)\] is :
a) \[4.00 × 10^{-6}M^{3}\]
b) \[4.00 × 10^{-7}M^{3}\]
c) \[5.00 × 10^{-6}M^{3}\]
d) \[5.00 × 10^{-7}M^{3}\]
Explanation:
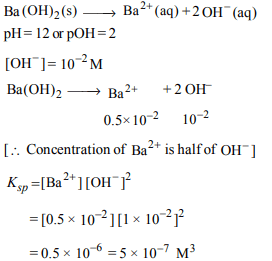
3. What is \[\left[H^{+}\right]\] in mol/L of a solution that is 0.20 M in \[CH_{3}COONa\] and 0.10 M in \[CH_{3}COOH\] ? \[K_{a}\] for \[CH_{3}COOH=1.8\times 10^{-5}\] .
a) \[3.5 × 10^{-4}\]
b) \[1.1 × 10^{-5}\]
c) \[1.8 × 10^{-5}\]
d) \[9.0 × 10^{-6}\]
Explanation:
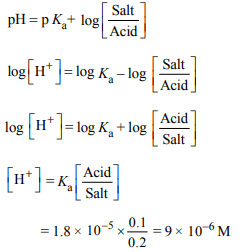
4. In a buffer solution containing equal concentration of \[B^{-}\]
and HB, the \[K_{b}\] for \[B^{-}\] is \[10^{-10}\] . The pH of buffer solution is :
a) 10
b) 7
c) 6
d) 4
Explanation:
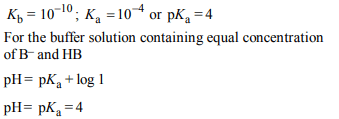
5. Which one of the following molecular hydrides acts as a Lewis
acid?
a) \[NH_{3}\]
b) \[H_{2}O\]
c) \[B_{2}H_{6}\]
d) \[CH_{4}\]
Explanation: Boron in B2H6 is electron deficient
6. A buffer solution is prepared in which the concentration of
\[NH_{3}\] is 0.30M and the concentration of \[NH_4^+\] is 0.20 M. If the
equilibrium constant, \[K_{b}\] for \[NH_{3}\] equals \[1.8\times 10^{-5}\] , what is
the pH of this solution ? (log 2.7 = 0.433).
a) 9.08
b) 9.43
c) 11.72
d) 8.73
Explanation:
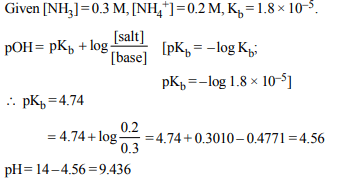
7. Which of the following is least likely to behave as Lewis
base ?
a) \[H_{2}O\]
b) \[NH_{3}\]
c) \[BF_{3}\]
d) \[OH^{-}\]
Explanation: BF3 behaves as lewis acid
8. In qualitative analysis, the metals of Group I can be separated
from other ions by precipitating them as chloride salts. A
solution initially contains \[Ag^{+}\] and \[Pb^{2+}\] at a concentration of
0.10 M. Aqueous HCl is added to this solution until the \[Cl^{-}\]
concentration is 0.10 M. What will the concentrations of \[Ag^{+}\] and \[Pb^{2+}\] be at equilibrium? \[(K_{sp}\] for AgCl = \[1.8 × 10^{-10},K_{sp}\] for \[PbCl_{2} = 1.7 × 10^{-5})\]
a) \[\left[Ag^{+}\right]= 1.8 × 10^{-7}M ;\left[Pb^{2+}\right]= 1.7 × 10^{-6}M\]
b) \[\left[Ag^{+}\right]= 1.8 × 10^{-11}M ;\left[Pb^{2+}\right]= 8.5 × 10^{-5}M\]
c) \[\left[Ag^{+}\right]= 1.8 × 10^{-9}M ;\left[Pb^{2+}\right]= 1.7 × 10^{-3}M\]
d) \[\left[Ag^{+}\right]= 1.8 × 10^{-11}M ;\left[Pb^{2+}\right]= 8.5 × 10^{-4}M\]
Explanation:
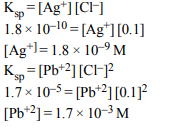
9. pH of a saturated solution of Ba(OH)2 is 12. The value of
solubility product \[\left(K_{sp}\right)\] of \[Ba\left(OH\right)_{2}\] is :
a) \[3.3 × 10^{-7}\]
b) \[5.0 × 10^{-7}\]
c) \[4.0 × 10^{-6}\]
d) \[5.0 × 10^{-6}\]
Explanation:
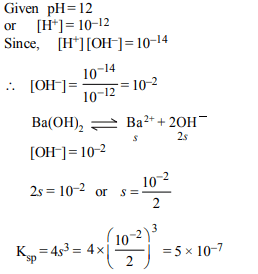
10. Buffer solutions have constant acidity and alkalinity because
a) these give unionised acid or base on reaction with added
acid or alkali.
b) acids and alkalies in these solutions are shielded from
attack by other ions
c) they have large excess of \[H^{+}\] or \[OH^{-}\] ions
d) they have fixed value of pH
Explanation:
