1. If the reaction between \[CO_{2}\] and \[H_{2}O\] is
\[CO_{2}+H_{2}O\rightleftharpoons H_{2} CO_{3} \rightleftharpoons H^{+}+HC\overline{O}_{3}\]
If \[CO_{2}\] escapes from the system
a) pH will decrease
b) \[H^{+}\] concentration will decrease
c) \[H_{2}CO_{3}\] concentration will be altered
d) The forward reaction is promoted
Explanation:
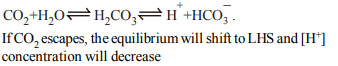
2. A solution contains 0.1 M \[H_{2}S\] and 0.3 M HCl, the
concentration of \[SH^{-}\] ions is \[\left(K_{a}=1\times 10^{-7}\right)\]
a) \[3.3\times 10^{-8}M\]
b) \[33\times 10^{-8}M\]
c) \[3.3\times 10^{-7}M\]
d) \[ 10^{-7}M\]
Explanation:
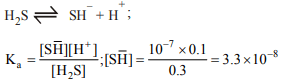
3. 20 ml of 0.2 M. NaOH are added to 50 ml of 0.2
M \[CH_{3}COOH\left(K_{a}=1.8\times 10^{-5}\right)\]
the pH of the solution is
a) 4.56
b) 4.73
c) 9.45
d) 6.78
Explanation:
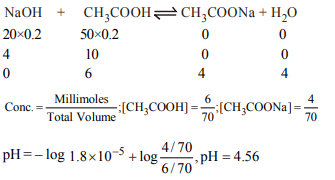
4. The pH at which the \[Mg \left(OH\right)_{2}\] begins to precipitate from a
solution containing 0.10 M \[Mg^{++}\] ions. The \[K_{sp}\] of \[Mg \left(OH\right)_{2}\] is \[1\times10^{-11}\]
a) 9
b) 5
c) 11
d) 4
Explanation:
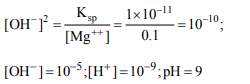
5. The 0.001M Solution of \[Mg \left(NO_{3}\right)_{2}\] is adjusted to pH 9, \[K_{sp}\] of \[Mg \left(OH\right)_{2}\] is \[8.9\times10^{-12}\] . At this pH
a) \[Mg \left(OH\right)_{2}\] will be precipitated
b) \[Mg \left(OH\right)_{2}\] is not precipitated
c) \[Mg \left(OH\right)_{3}\] will be precipitated
d) \[Mg \left(OH\right)_{3}\] is not precipitated
Explanation:
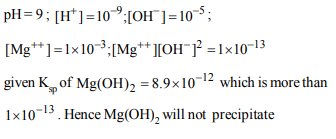
6. Calculate the pH of 0.5 M aqueous solution of NaCN, the \[pK_{b}\] of \[CN^{-}\] is 4.70
a) 4.70
b) 11.5
c) 7
d) 6.5
Explanation:
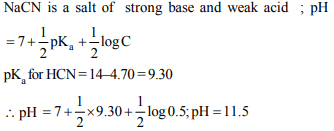
7. The pH of aqueous solution of 1M HCOONH4, \[pK_{a}\] of
HCOOH is 3.8 and \[pK_{b}\] of \[NH_{3}\] is 4.8
a) 6.5
b) 4.8
c) 3.8
d) 8.6
Explanation:
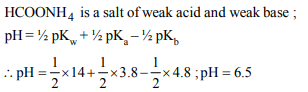
8. The hydrolysis of \[Na_{2}CO_{3}\] involves the reaction between
a) \[Na^{+}\] ions and water
b) \[Na^{+}\] and \[OH^{-}\] ions
c) \[CO_{3}^{2-}\] and \[H_{2}O\]
d) \[CO_{3}^{2-}\] and \[H^{+}\]
Explanation:
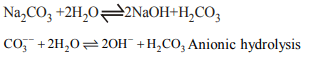
9. The solubility of \[BaF_{2}\] in a solution of \[Ba \left(NO_{3}\right)_{2}\] will be
represented by concentration term
a) \[\left[Ba^{2+}\right]\]
b) \[\left[F^{-}\right]\]
c) \[\frac{1}{2}\left[F^{-}\right]\]
d) \[2\left[NO_3^-\right]\]
Explanation:
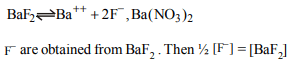
10. The enthalpy of neutralization of HCl and HCN by NaOH are
–55.9 and –12.1 kJ \[mol^{-1}\] respectively, the enthalpy of
ionisation of HCN is
a) - 43.8 kJ \[mol^{-1}\]
b) - 68.0 kJ \[mol^{-1}\]
c) 43.8 kJ \[mol^{-1}\]
d) 68.0 kJ \[mol^{-1}\]
Explanation: HCN is a weak acid and energy is required to affect its ionisation. Hence the enthalpy of neutralisation of HCN is less than the enthalpy of neutralisation of strong acid. The difference of enthalpy gives the enthalpy of ionisation. 55.9 kJ-12.1 kJ = 43.8 kJ